DelayQueue延迟队列之Java篇原创
1 DelayQueue 简介
- java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue是Java提供的一个延迟队列,数据是放在内存中的,JVM重启之后数据就全没了。
- 延迟队列的意思就是:放进队列里面的数据,不能立即被取出来。而是要等到指定的时间才能被取出来。这个时间是你自己指定的。
- 本篇代码示例基于java version “1.8.0_333”
2 少废话,先看代码
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
// 自己创建一个类MyDelay,实现Java提供的接口Delayed
public class MyDelay<T> implements Delayed {
// 延迟时间,(时间单位会在计算剩余时间的方法getDelay里面,由你自己指定,一般来说都会使用毫秒,更精确一点。)
long delayTime;
// 过期时间,(时间单位会在计算剩余时间的方法getDelay里面,由你自己指定,一般来说都会使用毫秒,更精确一点。)
long expire;
// 你自己放进队列里的数据
T data;
public MyDelay(long delayTime, TimeUnit delayTimeUnit, T t) {
// 将用户传进来的时间转换为毫秒
this.delayTime = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(delayTime, delayTimeUnit);
// 过期时间 = 当前时间 + 延迟时间(时间单位会在计算剩余时间的方法getDelay里面,由你自己指定,一般来说都会使用毫秒,更精确一点。)
// 当然你也可以使用别的时间,随意的
this.expire = System.currentTimeMillis() + delayTime;
data = t;
}
/**
* 剩余时间 = 过期时间 - 当前时间
*
*/
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
// 注意convert这个方法,第一个参数是一个long类型的数值,第二个参数的意思是告诉convert第一个long类型的值的单位是毫秒
return unit.convert(this.expire - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
/**
* 优先级:俩个任务比较,时间短的优先执行
*
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o){
long f = this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) - o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return (int)f;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// 这个toString()方法不是必须的,你可以不重写。写不写都无所谓,我这里为了测试,将数据打印出来了。
return "delayTime=" + delayTime + ",expire=" + expire + ",data=" + data;
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
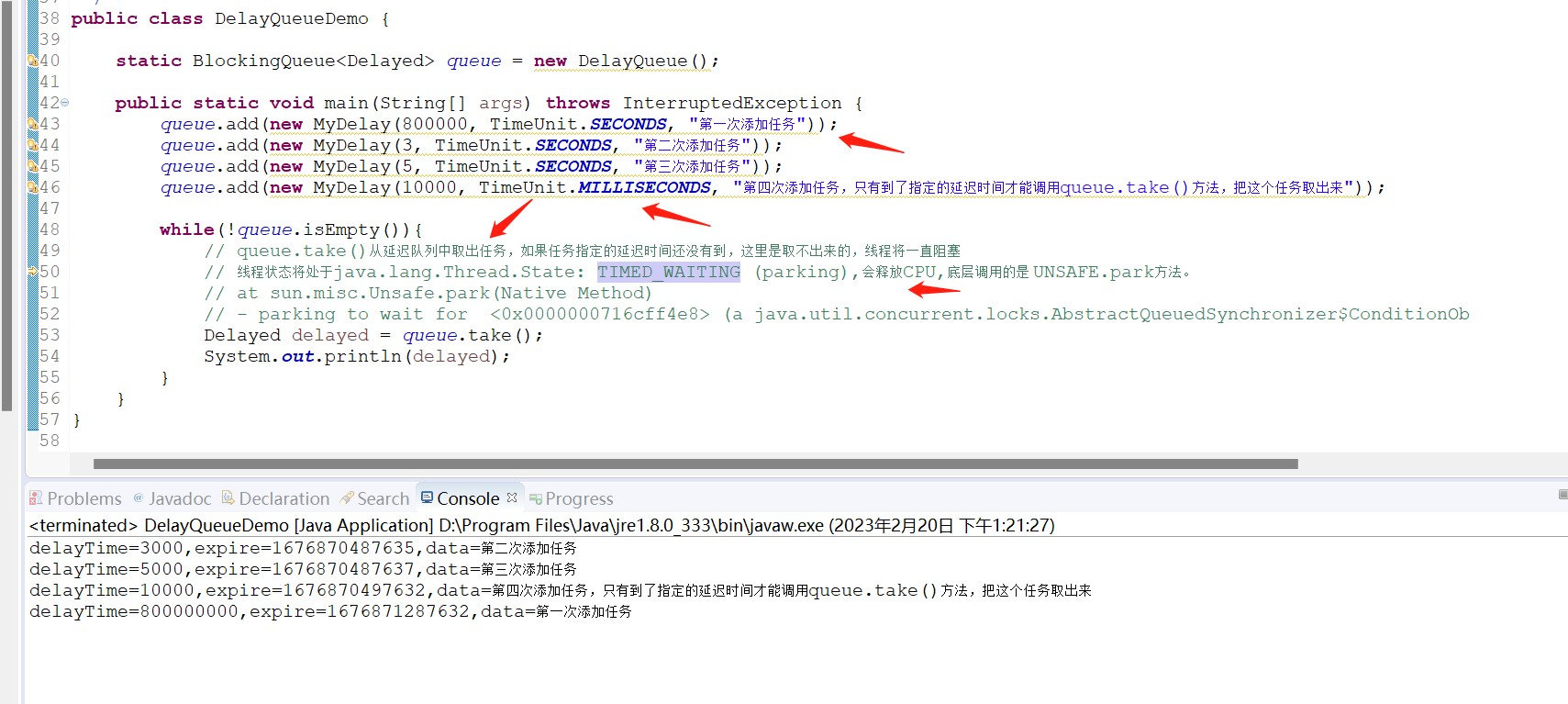
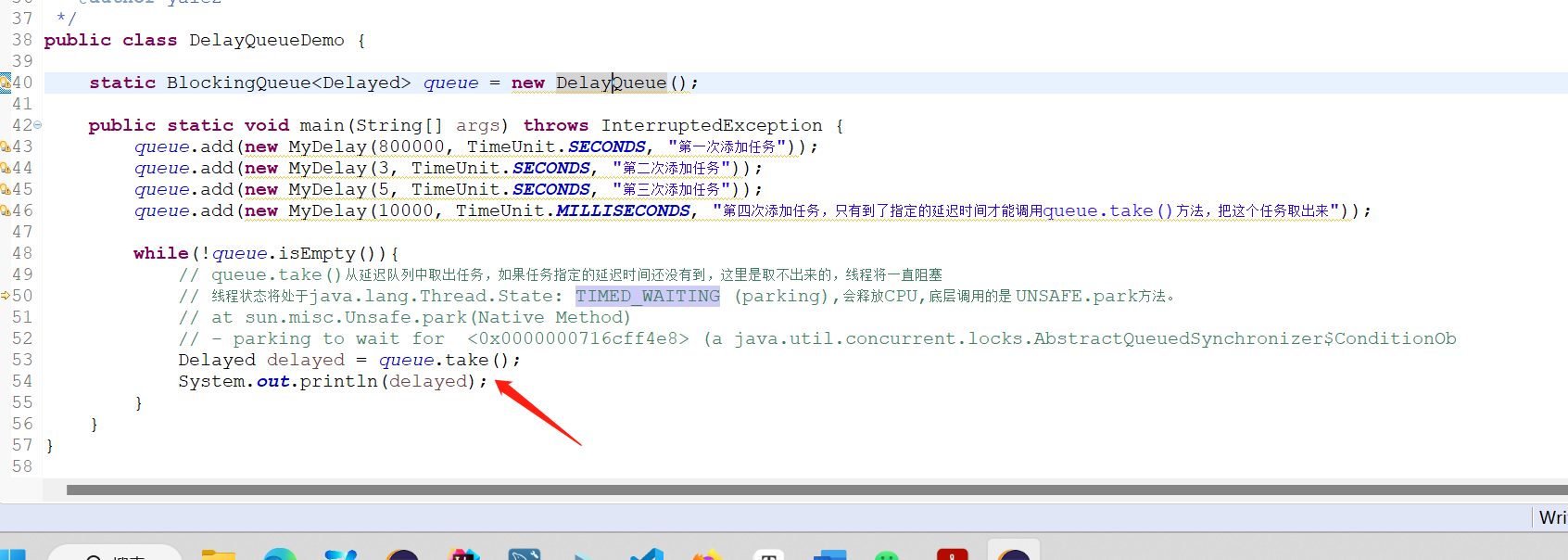
public class DelayQueueDemo {
static BlockingQueue<Delayed> queue = new DelayQueue();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
queue.add(new MyDelay(800000, TimeUnit.SECONDS, "第一次添加任务"));
queue.add(new MyDelay(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS, "第二次添加任务"));
queue.add(new MyDelay(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS, "第三次添加任务"));
queue.add(new MyDelay(10000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, "第四次添加任务,只有到了指定的延迟时间才能调用queue.take()方法,把这个任务取出来"));
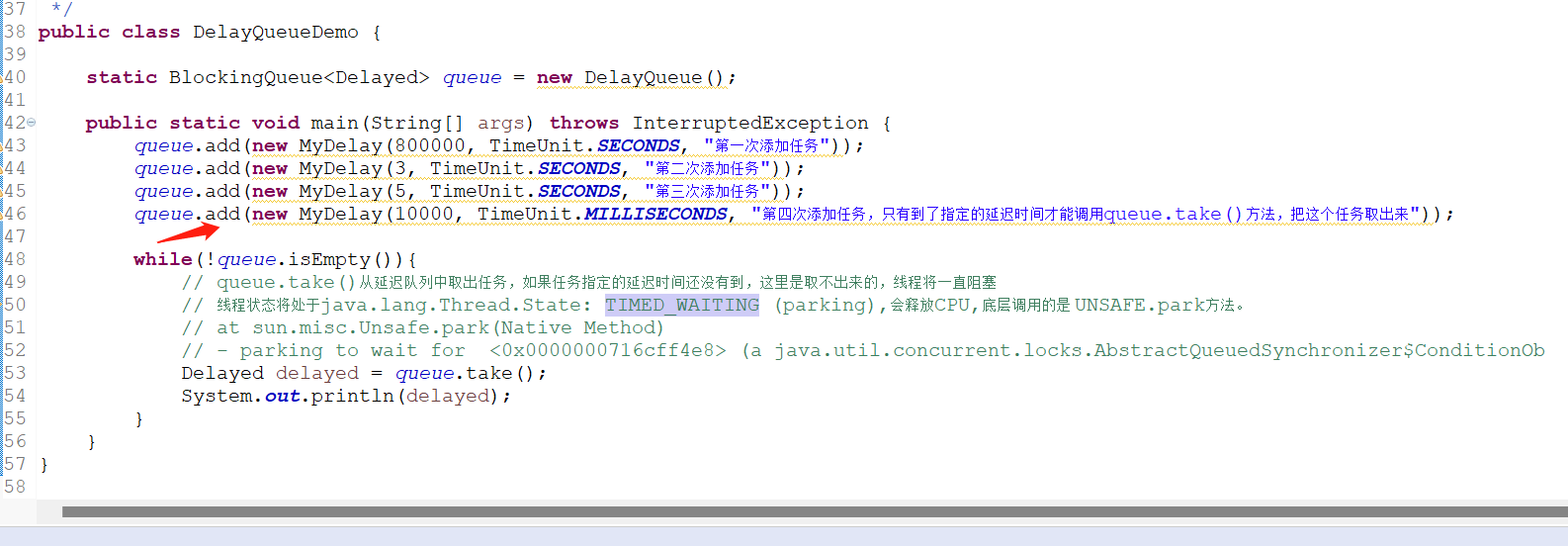
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
// queue.take()从延迟队列中取出任务,如果任务指定的延迟时间还没有到,这里是取不出来的,线程将一直阻塞
// 线程状态将处于java.lang.Thread.State: TIMED_WAITING (parking),会释放CPU,底层调用的是 UNSAFE.park方法。
Delayed delayed = queue.take();
System.out.println(delayed);
}
}
}
3 解析代码
3.1 先看java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue的源码
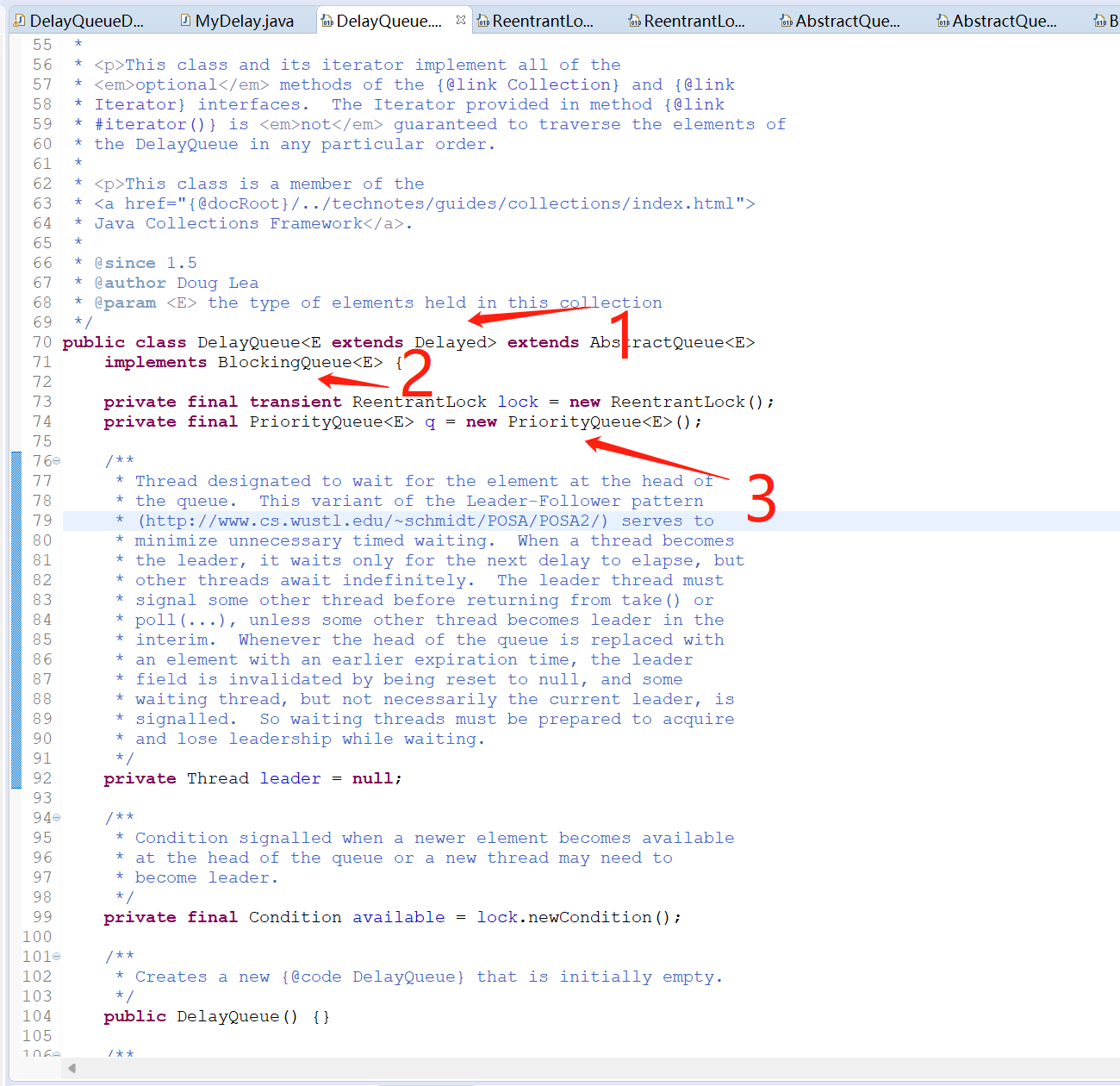
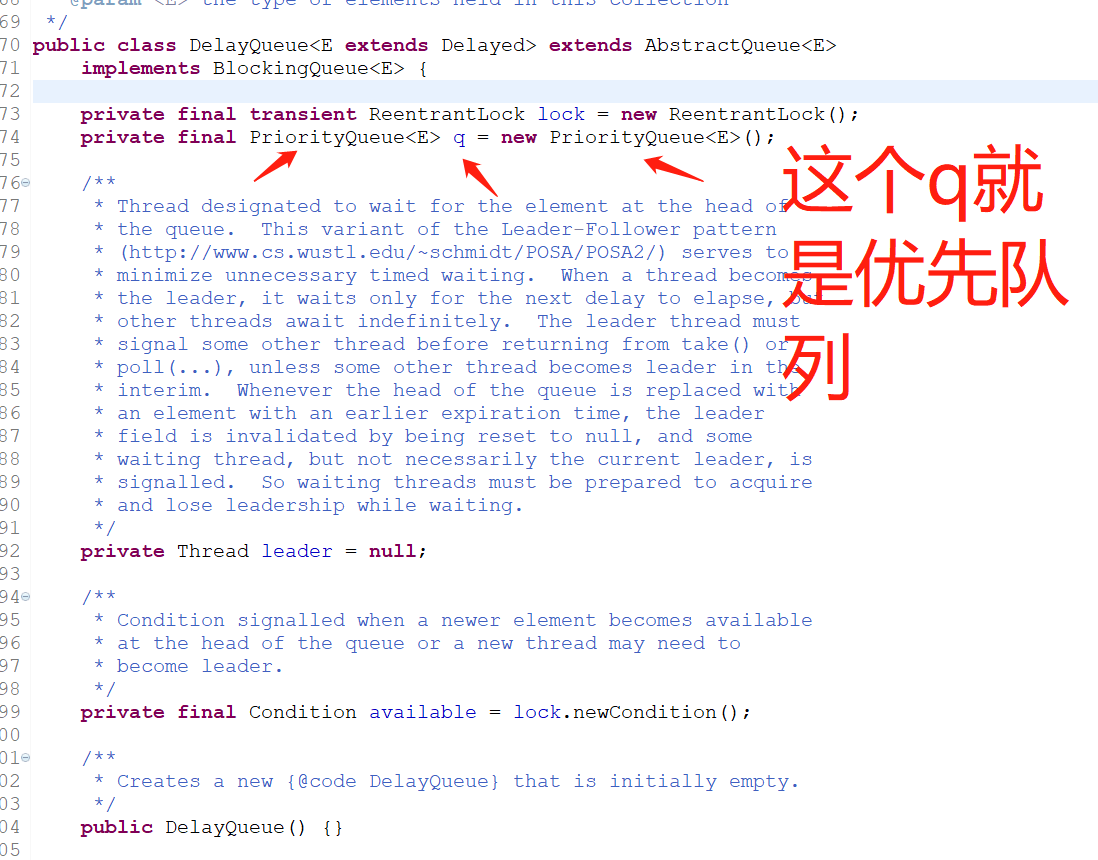
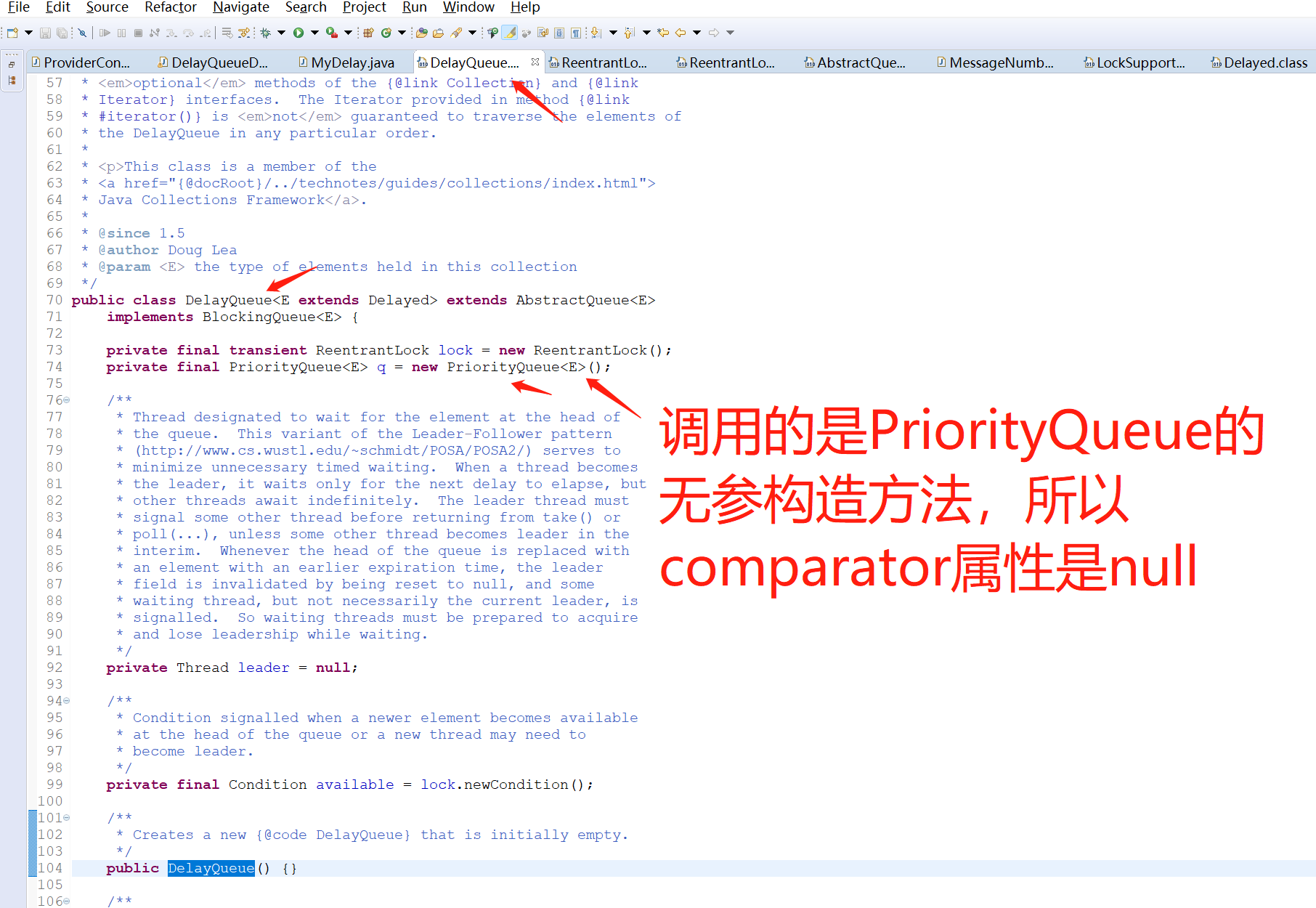
3.1.1 注意上图第一个地方,DelayQueue<E extends Delayed>
DelayQueue延迟队列要求元素必须是Delayed或者是Delayed的子类。而Delayed是一个接口,所以我们要先创建一个类MyDelay去实现Delayed这个接口。
Delayed的源码如下:
package java.util.concurrent;
/**
* A mix-in style interface for marking objects that should be
* acted upon after a given delay.
*
* <p>An implementation of this interface must define a
* {@code compareTo} method that provides an ordering consistent with
* its {@code getDelay} method.
*
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
*/
public interface Delayed extends Comparable<Delayed> {
/**
* Returns the remaining delay associated with this object, in the
* given time unit.
*
* @param unit the time unit
* @return the remaining delay; zero or negative values indicate
* that the delay has already elapsed
*/
long getDelay(TimeUnit unit);
}
这个接口里面只定义了一个方法long getDelay(TimeUnit unit);
看方法的返回值备注:the remaining delay; zero or negative values indicate that the delay has already elapsed。意思为:剩余的延迟;零或负值表示延迟已过。
我们要想办法把这个方法的返回值计算出来,所以我们在MyDelay类中定义了俩个属性delayTime(延迟时间)和expire(过期时间)。
延迟时间:这个时间是我们自己指定的,通过MyDelay的构造方法传进来的。就是你希望元素在放进DelayQueue延迟队列之后多长时间才能被取出来消费。
当前时间:我们不能光说延迟时间,比如你说延迟30分钟。那你是要在哪个时间点的基础上,往后延迟30分钟。我们代码中是基于当前时间往后延迟的。
过期时间 = 当前时间 + 延迟时间。
剩余时间 = 过期时间 - 当前时间。
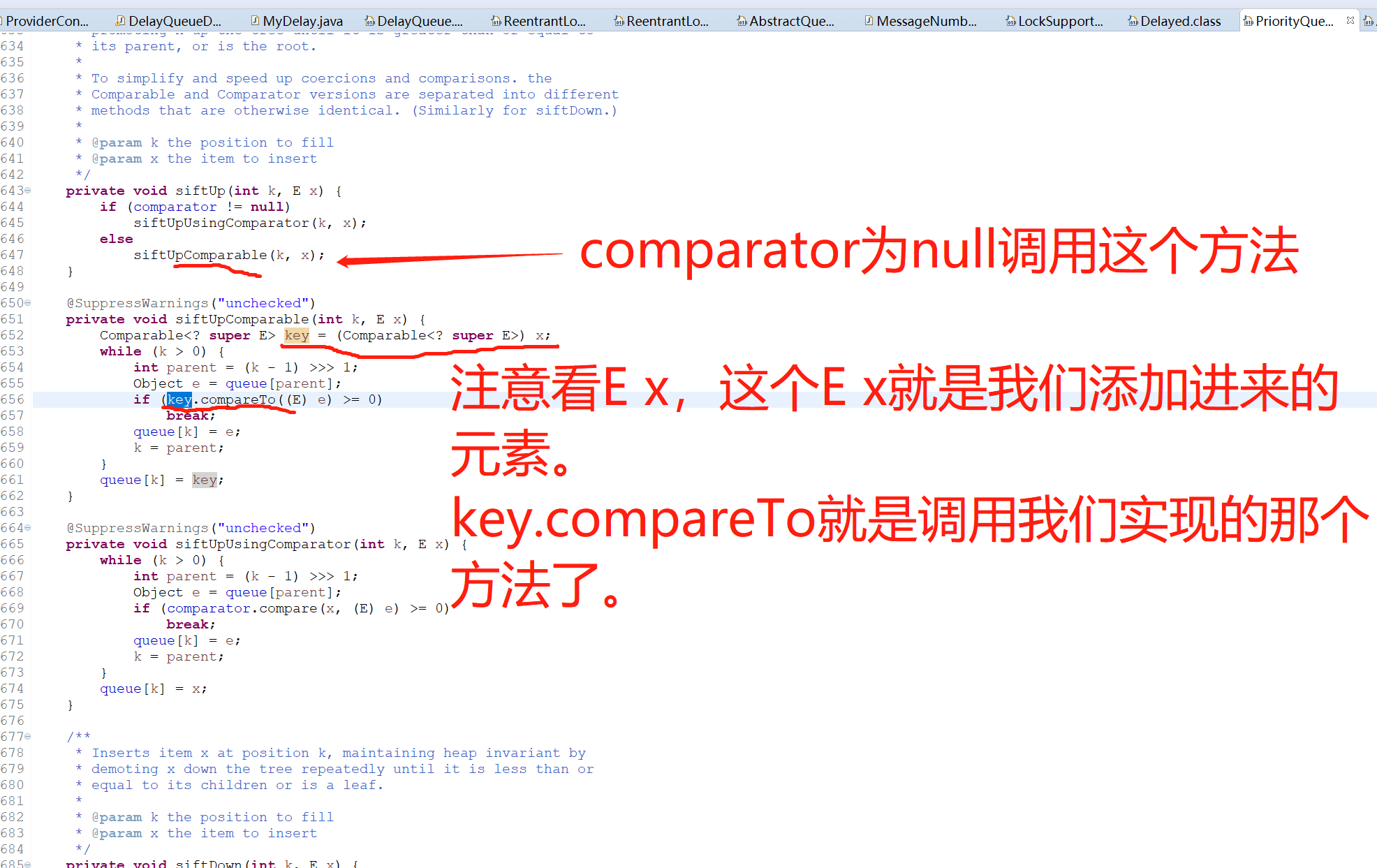
注意:Delayed这个接口还继承了Comparable接口,所以我们还需要实现一个compareTo方法,用来比较DelayQueue延迟队列里面的元素,哪个元素的优先级是最高(哪个元素最先过期),就把最先过期的元素放在队列的最前面。
3.1.2 注意上图第二个地方,implements BlockingQueue<E>
DelayQueue实现了BlockingQueue(阻塞队列)接口,所以本质上延迟队列也是一个阻塞队列。
3.1.3 注意上图第三个地方,PriorityQueue<E> q = new PriorityQueue<E>();
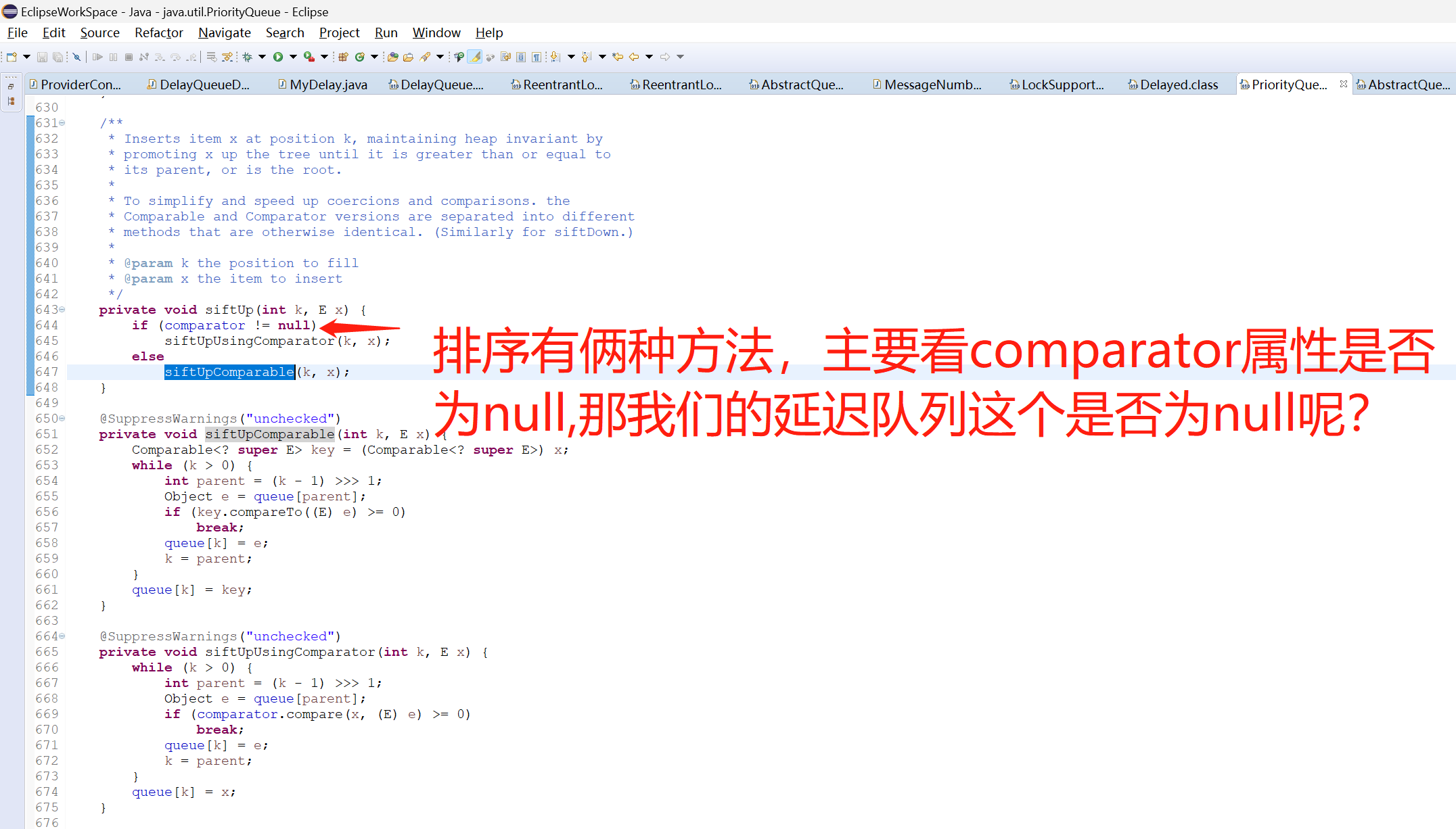
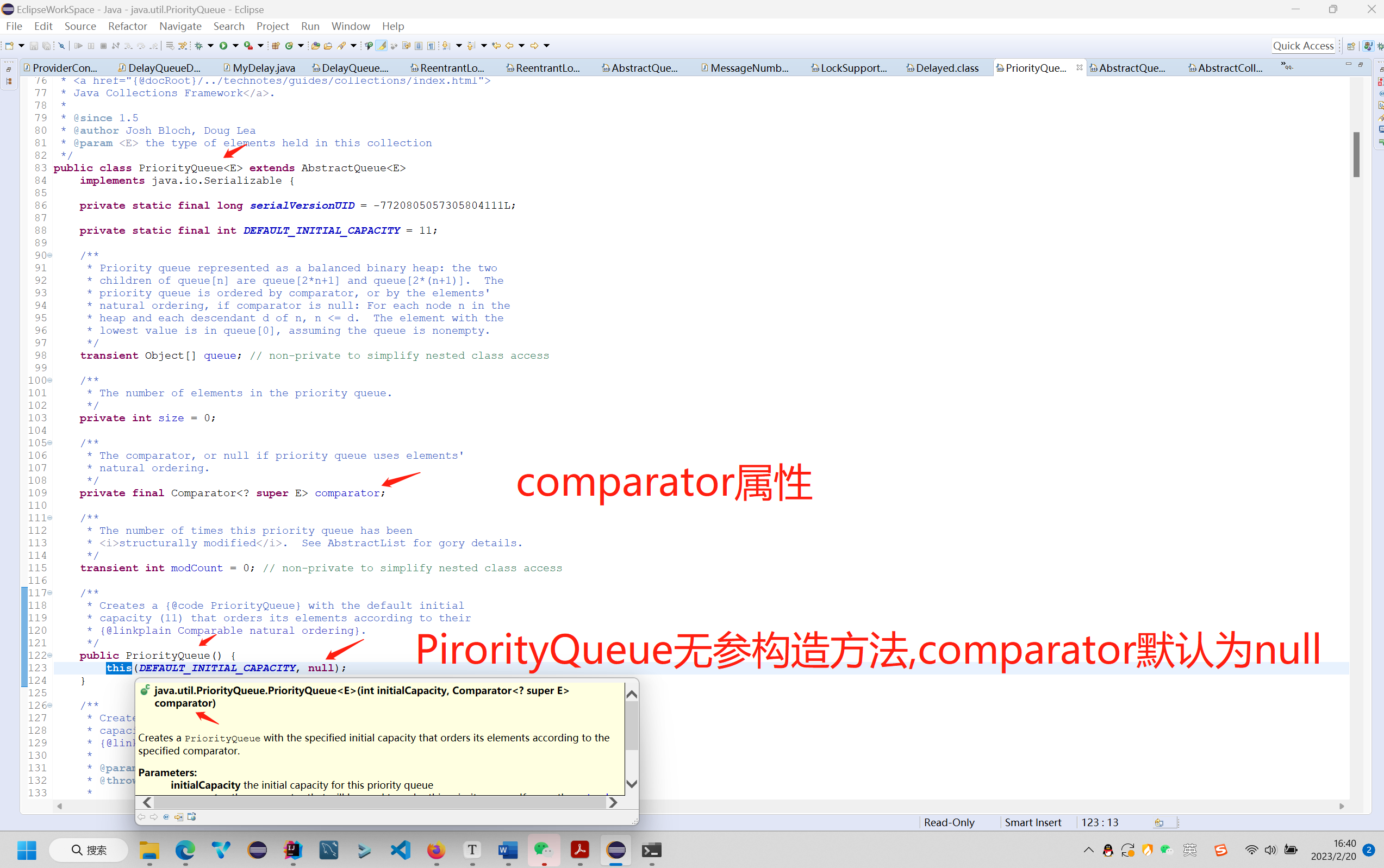
DelayQueue类有一个属性PriorityQueue(优先级队列),这个优先级队列就是依赖我们MyDelay类实现的compareTo方法去给添加到队列里面的元素做一个排序(优先级),哪个元素最先过期,哪个元素的优先级就最高,哪个元素就会排在最前面,就会被最先从队列里面取出来。
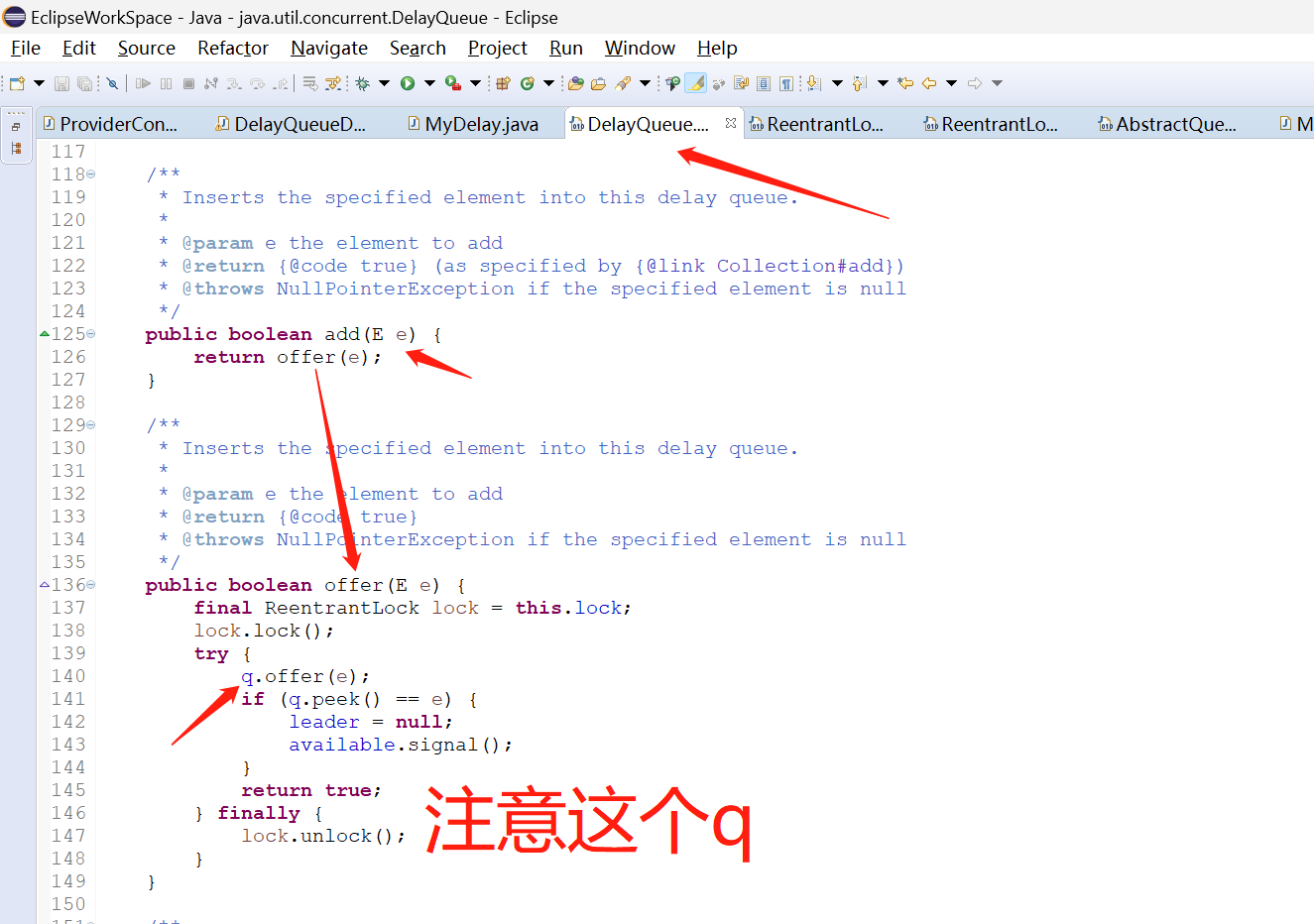
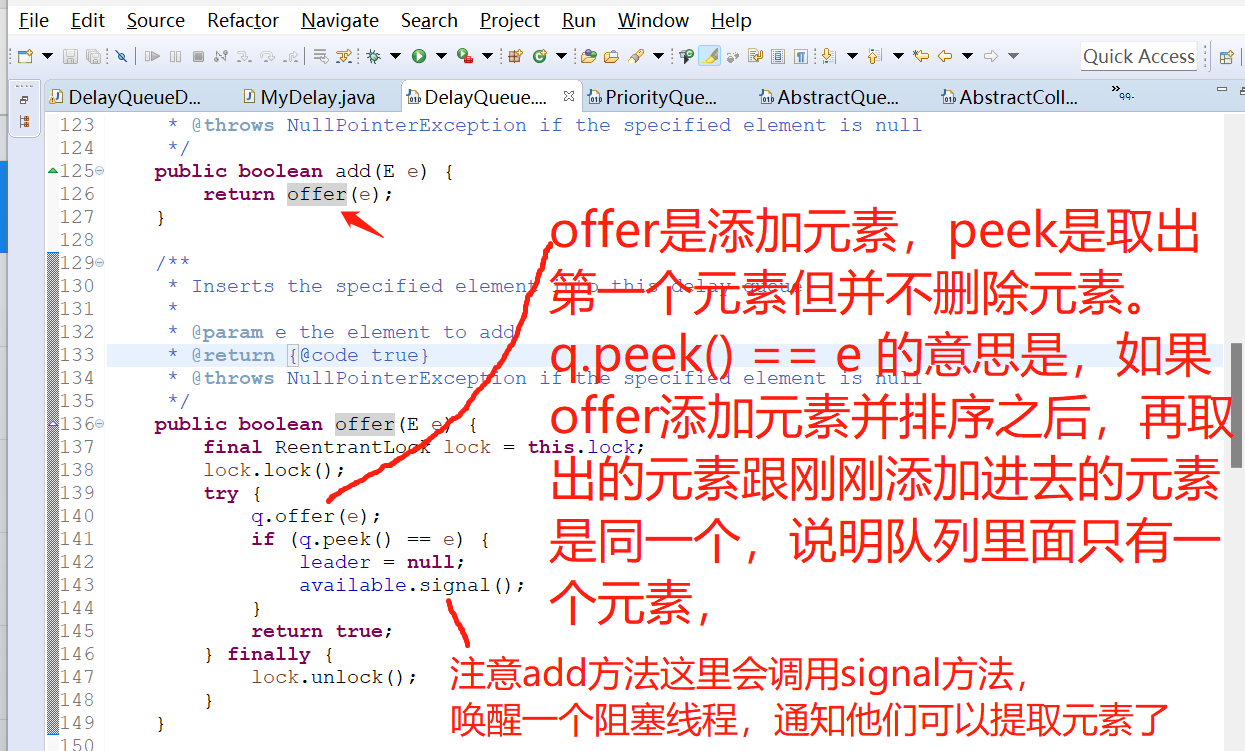
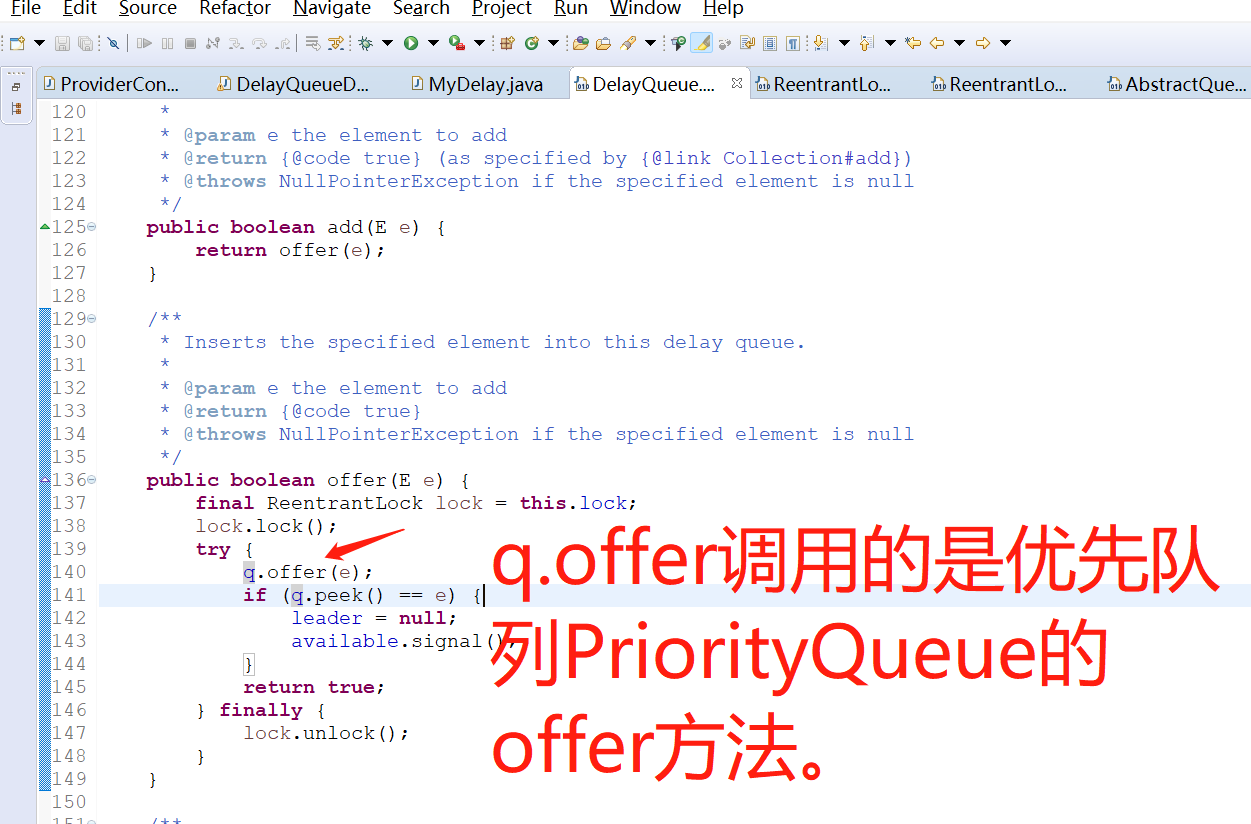
3.2 java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue添加元素add方法的源码
所以,DelayQueue延迟队列的add方法最终调用的还是PriorityQueue这个优先队列的offer方法,数据最终是存在PriorityQueue这个优先队列里面了。
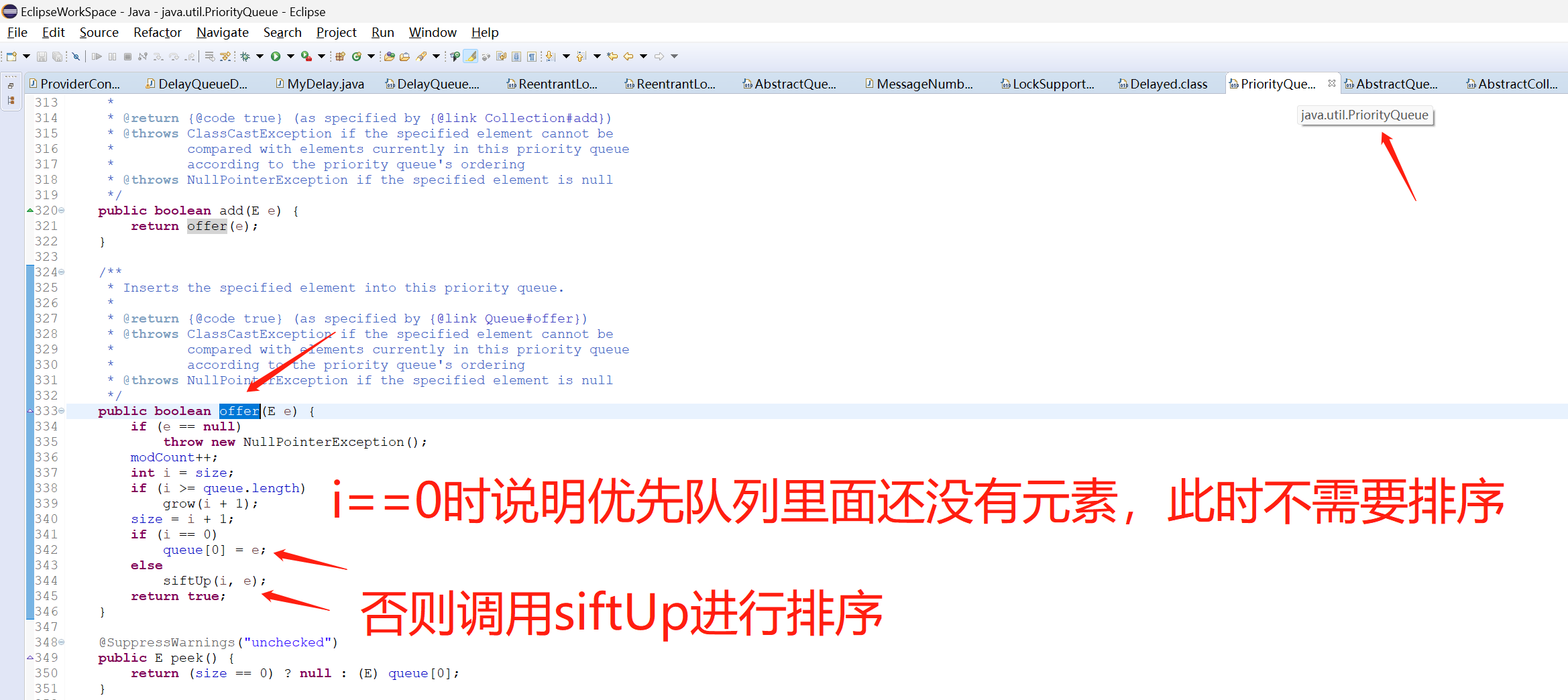
3.3 java.util.PriorityQueue优先队列添加元素add方法的源码
所以元素的排序是在DelayQueue延迟队列在添加元素的时候,而不是在DelayQueue取出元素的时候排序的。
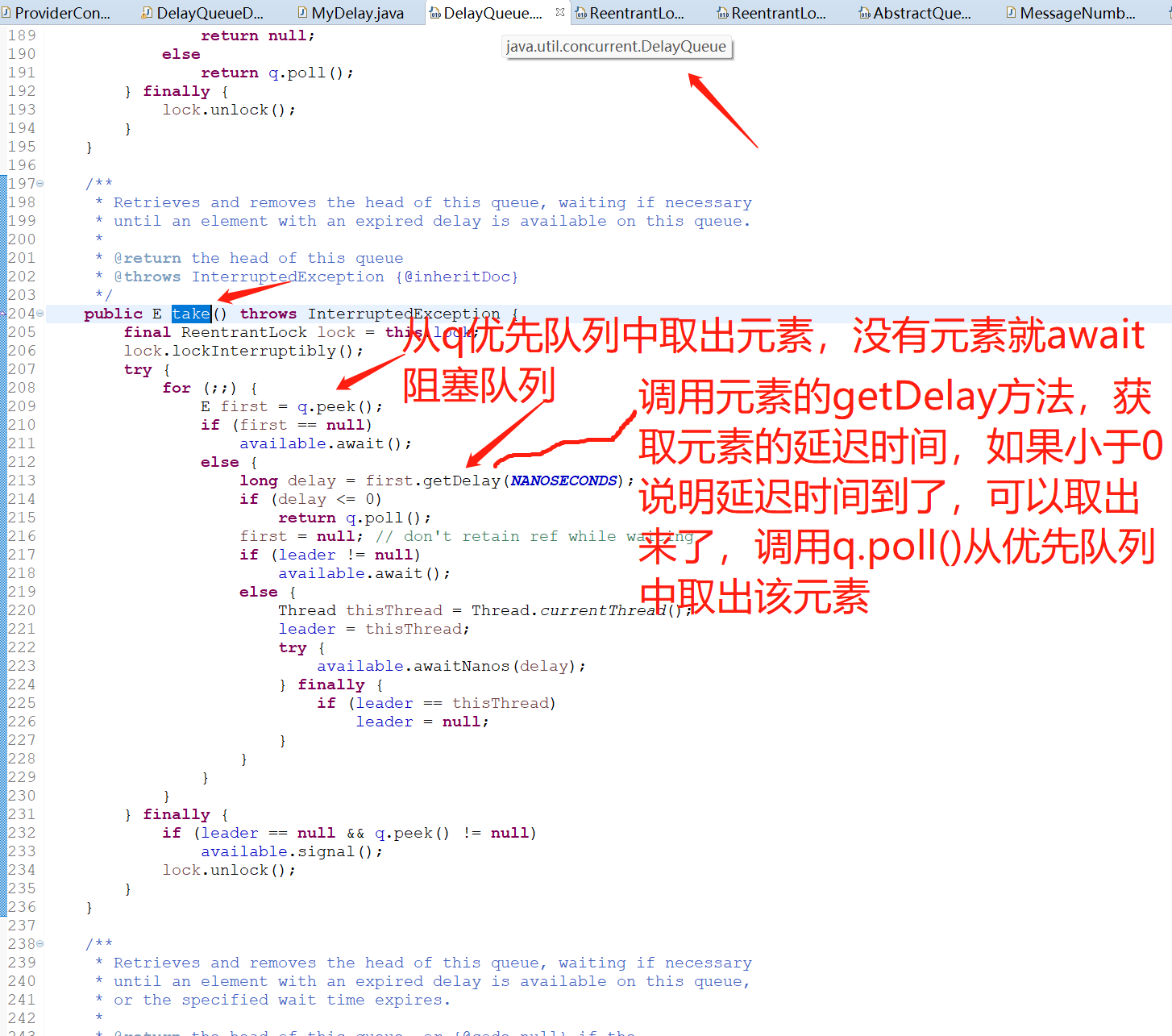
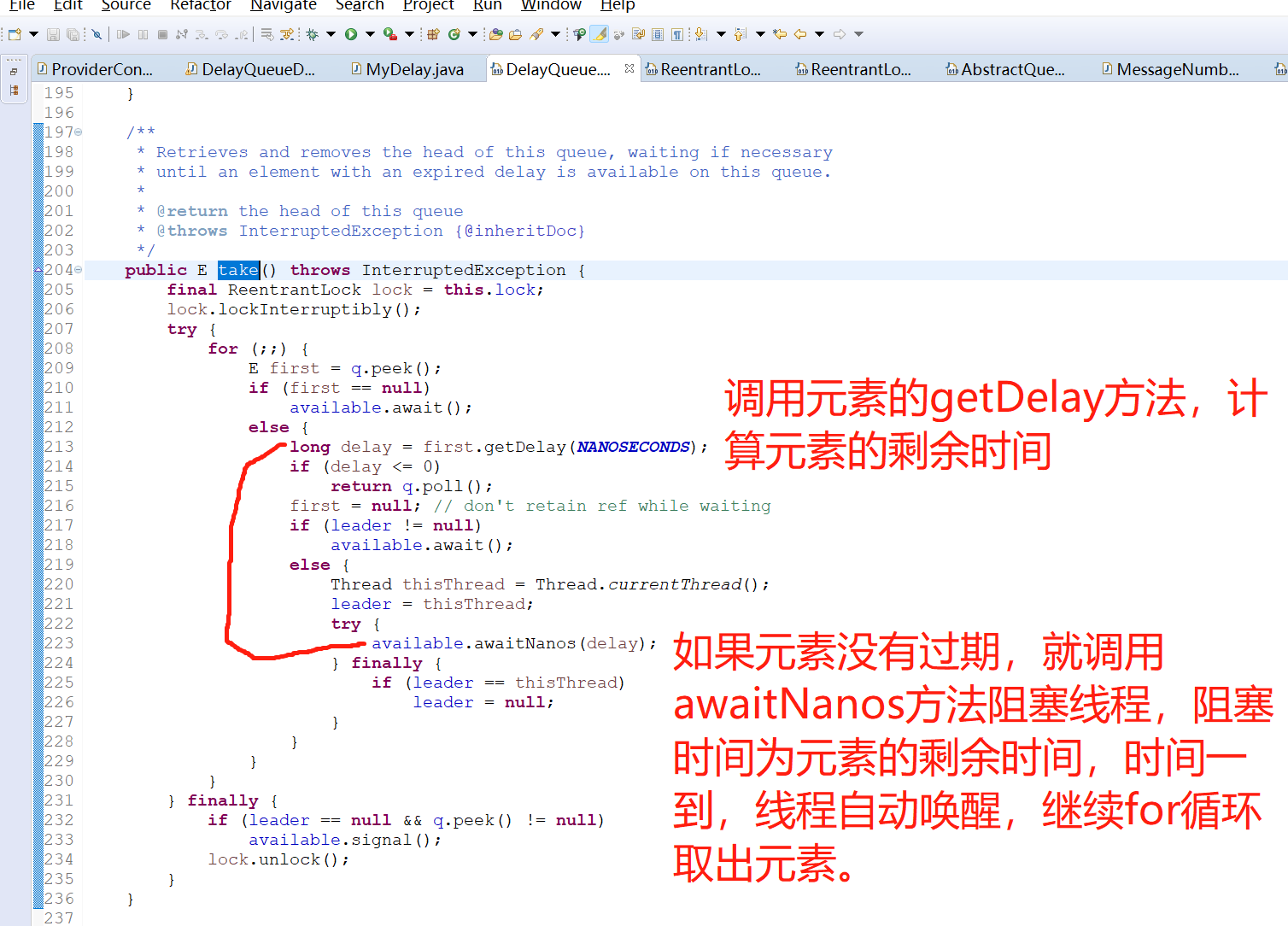
3.4 java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue取元素take方法的源码