JDBC PreparedStatement 字段值为null导致TBase带宽飙升的案例分析原创
问题描述
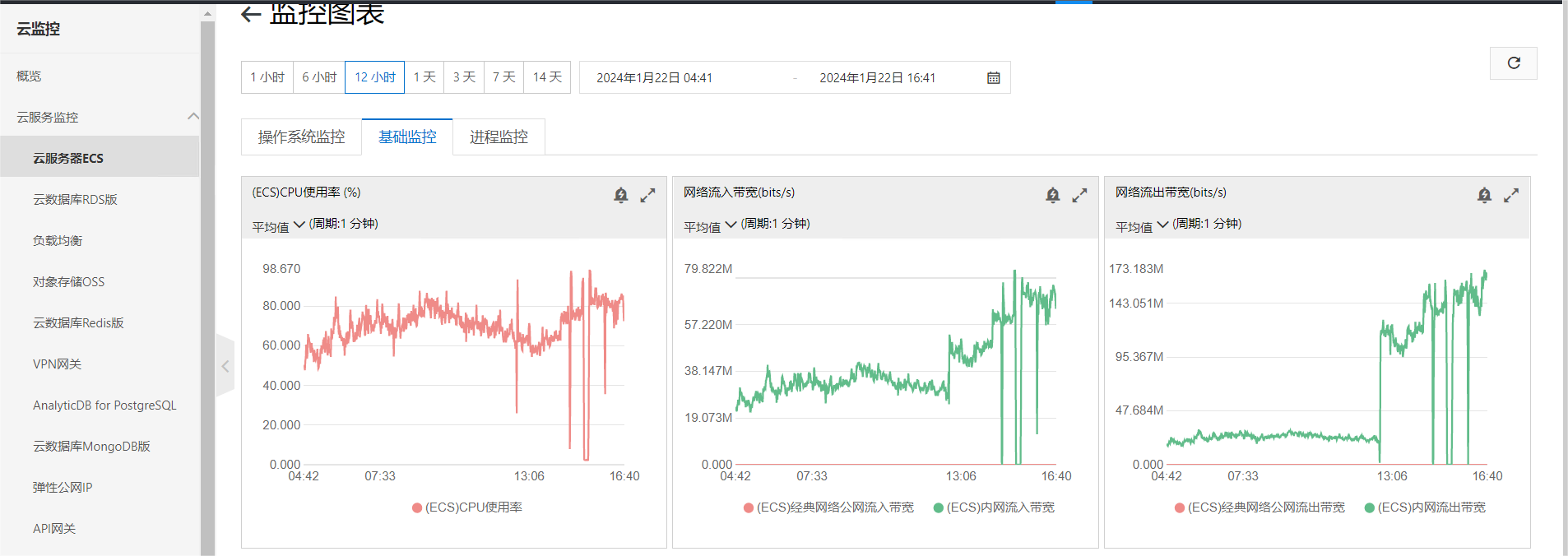
某产品线的某个RocketMQ GroupID消息大量积压;DBA反馈该应用使用的TBase数据库带宽流量飙升,TBase数据库的CPU、Load处于正常范围。
问题分析
应用逻辑
该应用主要逻辑是从RocketMQ接收消息,如果该消息在TBase中不存在,则插入相关信息到TBase中;如果该消息在TBase中存在,则更新相关信息。
主要执行的SQL类似下面这个样子:
update test set a = ?,b = ?,c = ? where d = ?
TBase JDBC Driver
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<version>42.3.3</version>
</dependency>
无灰度不变更
检查该应用变更记录,发现该应用是在12点40分左右开始变更的,与问题产生时间吻合,所以回滚应用,但是回滚之后问题依旧存在;
检查该应用配置变更记录,发现该应用最近一次配置变更是2023年12月20日,配置变更之后,发过几次发版,排除配置变更导致故障的情况。
TBase数据库飙升的带宽来自哪里?
检查该应用ECS出口带宽在12点40分左右开始飙升,与TBASE数据库带宽飙升时间吻合。
TBase带宽打满会导致消息处理变慢,从RocketMQ控制台监控指标也可以说明这一点。
消息处理变慢意味着打到TBase的请求减少了,但是带宽却增加了很多,意味着打到TBase的一个请求的字节数增大了,所以关键是需要分析出针对一个请求增加了哪些字节。
为了便于理解,首先介绍下TBase中与本案例相关的通信协议(内容来自网络)。
Extended Query
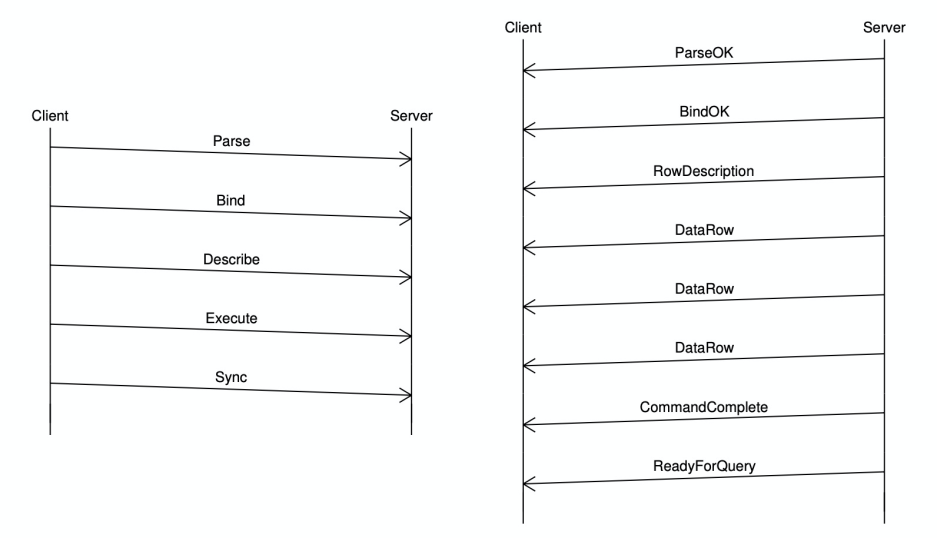
Extended Query 协议将以上 Simple Query 的处理流程分为若干步骤,每一步都由单独的服务端消息进行确认。该协议可以使用服务端的 perpared-statement 功能,即先发送一条参数化 SQL,服务端收到 SQL(Statement)之后对其进行解析、重写并保存,这里保存的 Statement 也就是所谓 Prepared-statement,可以被复用;执行 SQL 时,直接获取事先保存的 Prepared-statement 生成计划并执行,避免对同类型 SQL 重复解析和重写。
如下例, SELECT * FROM users u, logs l WHERE u.usrid=$1 AND u.usrid=l.usrid AND l.date = $2; 是一条参数化 SQL,执行 PREPARE 时,服务端对该 SQL 进行解析和重写;执行 EXECUTE 时,为 Prepared Statement 生成计划并执行。第二次执行 EXECUTE 时无需再对 SQL 进行解析和重写,直接生成计划并执行即可。
可见,Extended Query 协议通过使用服务端的 Prepared Statement,提升同类 SQL 多次执行的效率。但与 Simple Query 相比,其不允许在一个请求中包含多条 SQL 命令,否则会报语法错误。
Extended Query 协议通常包括 5 个步骤,分别是 Parse,Bind,Describe,Execute 和 Sync。以下分别介绍各个阶段的处理流程。
Parse
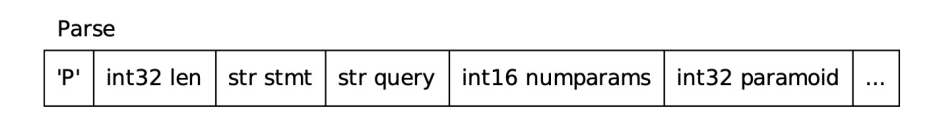
客户端首先向服务端发送一个 Parse 消息,该消息包括参数化 SQL,参数占位符以及每个参数的类型,还可以指定 Statement 的名字,若不指定名字,即为一个 “未命名” 的 Statement,该 Statement 会在生成下一个 “未命名” Statement 时予以销毁,若指定名字,则必须在下次发送 Parse 消息前将其显式销毁。
PostgreSQL 服务端收到该消息后,调用 exec_parse_message 函数进行处理,进行语法分析、语义分析和重写,同时会创建一个 Plan Cache 的结构,用于缓存后续的执行计划。
Bind
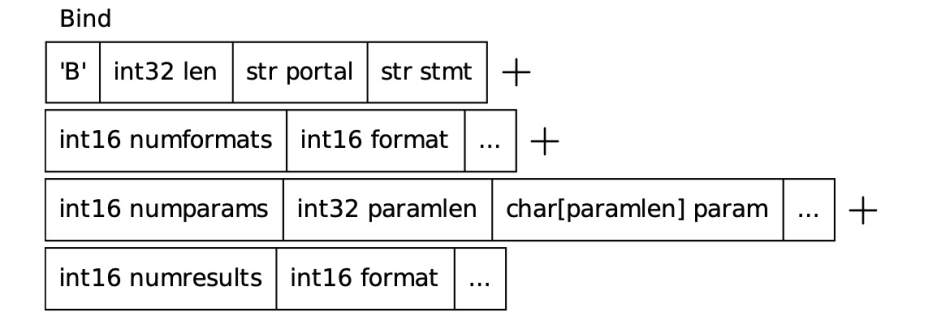
客户端发送 Bind 消息,该消息携带具体的参数值、参数格式和返回列的格式,如下:
PostgreSQL 收到该消息后,调用 exec_bind_message 函数进行处理。为之前保存的 Prepared Statement 创建执行计划并将其保存在 Plan Cache 中,创建一个 Portal 用于后续执行。关于 Plan Cache 的具体实现和复用逻辑在此不细述,以后单独撰文介绍。
在 PostgreSQL 内核中,Portal 是对查询执行状态的一种抽象,该结构贯穿执行器运行的始终。
Describe
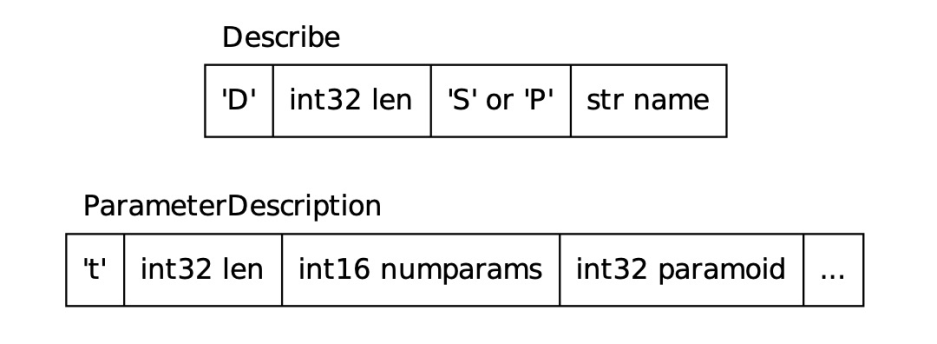
客户端可以发送 Describe 消息获取 Statment 或 Portal 的元信息,即返回结果的列名,类型等信息,这些信息由 RowDescription 消息携带。如果请求获取 Statement 的元信息,还会返回具体的参数信息,由 ParameterDescription 消息携带。
Execute
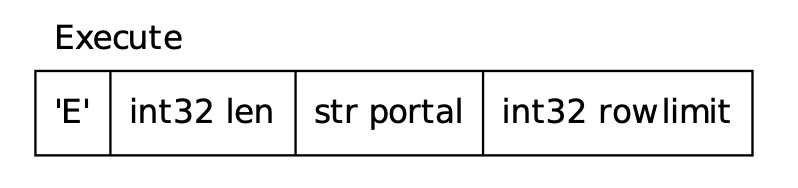
客户端发送 Execute 消息告知服务端执行请求,服务端收到消息后,执行 Bind 阶段创建的 Portal,执行结果通过 DataRow 消息返回给客户端,执行完成后发送 CommandComplete 。
Execute 消息中可以指定返回的行数,若行数为 0,表示返回所有行。
Sync
使用 Extended Query 协议时,一个请求总是以 Sync 消息结束,服务端接收到 Sync 消息后,关闭隐式开启的事务并回复 ReadyForQuery 消息。
Extended Query 完整的消息流如下:
所以接下来的思路是tcpdump抓包,然后通过wireshark分析出一个请求发送了哪些报文到TBase就可以基本确认问题了。
可惜的是抓的包wireshark并不能识别出TBase协议;另一个思路是TBase服务端能不能分析出一个请求具体涉及哪些报文,TBase技术支持最终没有提供出来,至此通过分析报文的方式没有走通。
另外一个思路是从应用程序侧分析TBase JDBC Driver发送请求的逻辑。
TBase JDBC Driver
通过分析Driver相关代码,找出Driver请求TBase相关逻辑,然后抓取运行时一些参数。
通过arthas抓包发现在PreparedStatement.executeUpdate()真正执行之前,Driver似乎就像TBase服务端发送了报文:
以上这个点是很可疑的,所以接下来抓取调用栈:
ts=2024-01-23 00:23:56;thread_name=ConsumeMessageThread_12;id=14a;is_daemon=false;priority=5;TCCL=org.apache.catalina.loader.ParallelWebappClassLoader@246b0ff2;trace_id=0a04cb0d17059202723904892d7747;rpc_id=0.1.10.1.104207185.11933.1.10413251.1.1.104216118.1.1.10413223
@org.postgresql.core.v3.QueryExecutorImpl.sendQuery()
at org.postgresql.core.v3.QueryExecutorImpl.execute(QueryExecutorImpl.java:347)
at org.postgresql.core.v3.QueryExecutorImpl.execute(QueryExecutorImpl.java:315)
at org.postgresql.jdbc.PgPreparedStatement.getParameterMetaData(PgPreparedStatement.java:1659)
at com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidPooledPreparedStatement.getParameterMetaData(DruidPooledPreparedStatement.java:710)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.StatementCreatorUtils.setNull(StatementCreatorUtils.java:276)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.StatementCreatorUtils.setParameterValueInternal(StatementCreatorUtils.java:235)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.StatementCreatorUtils.setParameterValue(StatementCreatorUtils.java:169)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.ArgumentPreparedStatementSetter.doSetValue(ArgumentPreparedStatementSetter.java:66)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.ArgumentPreparedStatementSetter.setValues(ArgumentPreparedStatementSetter.java:47)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate$2.doInPreparedStatement(JdbcTemplate.java:875)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate$2.doInPreparedStatement(JdbcTemplate.java:870)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate.execute(JdbcTemplate.java:633)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate.update(JdbcTemplate.java:870)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate.update(JdbcTemplate.java:931)
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate.update(JdbcTemplate.java:941)
at xxxxx
at com.aliyun.openservices.ons.api.impl.rocketmq.ConsumerImpl$MessageListenerImpl.consumeMessage(ConsumerImpl.java:116)
at com.alibaba.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService$ConsumeRequest.run(ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.java:710)
at java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter.call(Executors.java:511)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:266)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1142)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:617)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
接下来重点分析下调用栈,为了便于说明,以上调用栈的复现可以用如下代码表示:
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JdbcTemplateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("org.postgresql.Driver");
dataSource.setUsername("postgres");
dataSource.setPassword("admin");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgres");
dataSource.setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(10 * 60 * 1000);
dataSource.setInitialSize(0);
dataSource.setPhyTimeoutMillis(1000);
dataSource.setTestWhileIdle(false);
dataSource.setFilters("stat");
dataSource.init();
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
String sql = "update test set name = ?,address = ? where id = ?";
Object[] params = new Object[3];
params[0] = null;
params[1] = null;
params[2] = 1;
int size = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,params);
System.out.println(size);
}
}
按照线程栈的调用关系,以此分析相关类的代码:
ArgumentPreparedStatementSetter
public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
if (this.args != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.args.length; i++) {
Object arg = this.args[i];
doSetValue(ps, i + 1, arg);
}
}
}
protected void doSetValue(PreparedStatement ps, int parameterPosition, Object argValue) throws SQLException {
if (argValue instanceof SqlParameterValue) {
SqlParameterValue paramValue = (SqlParameterValue) argValue;
StatementCreatorUtils.setParameterValue(ps, parameterPosition, paramValue, paramValue.getValue());
}
else {
StatementCreatorUtils.setParameterValue(ps, parameterPosition, SqlTypeValue.TYPE_UNKNOWN, argValue);
}
}
StatementCreatorUtils
private static void setParameterValueInternal(PreparedStatement ps, int paramIndex, int sqlType,
String typeName, Integer scale, Object inValue) throws SQLException {
String typeNameToUse = typeName;
int sqlTypeToUse = sqlType;
Object inValueToUse = inValue;
// override type info?
if (inValue instanceof SqlParameterValue) {
SqlParameterValue parameterValue = (SqlParameterValue) inValue;
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding type info with runtime info from SqlParameterValue: column index " + paramIndex +
", SQL type " + parameterValue.getSqlType() + ", type name " + parameterValue.getTypeName());
}
if (parameterValue.getSqlType() != SqlTypeValue.TYPE_UNKNOWN) {
sqlTypeToUse = parameterValue.getSqlType();
}
if (parameterValue.getTypeName() != null) {
typeNameToUse = parameterValue.getTypeName();
}
inValueToUse = parameterValue.getValue();
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Setting SQL statement parameter value: column index " + paramIndex +
", parameter value [" + inValueToUse +
"], value class [" + (inValueToUse != null ? inValueToUse.getClass().getName() : "null") +
"], SQL type " + (sqlTypeToUse == SqlTypeValue.TYPE_UNKNOWN ? "unknown" : Integer.toString(sqlTypeToUse)));
}
if (inValueToUse == null) {
setNull(ps, paramIndex, sqlTypeToUse, typeNameToUse);
}
else {
setValue(ps, paramIndex, sqlTypeToUse, typeNameToUse, scale, inValueToUse);
}
}
private static void setNull(PreparedStatement ps, int paramIndex, int sqlType, String typeName) throws SQLException {
if (sqlType == SqlTypeValue.TYPE_UNKNOWN || sqlType == Types.OTHER) {
boolean useSetObject = false;
Integer sqlTypeToUse = null;
DatabaseMetaData dbmd = null;
String jdbcDriverName = null;
boolean tryGetParameterType = true;
if (shouldIgnoreGetParameterType == null) {
try {
dbmd = ps.getConnection().getMetaData();
jdbcDriverName = dbmd.getDriverName();
tryGetParameterType = !driversWithNoSupportForGetParameterType.contains(jdbcDriverName);
if (tryGetParameterType && jdbcDriverName.startsWith("Oracle")) {
// Avoid getParameterType use with Oracle 12c driver by default:
// needs to be explicitly activated through spring.jdbc.getParameterType.ignore=false
tryGetParameterType = false;
driversWithNoSupportForGetParameterType.add(jdbcDriverName);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.debug("Could not check connection metadata", ex);
}
}
else {
tryGetParameterType = !shouldIgnoreGetParameterType;
}
if (tryGetParameterType) {
try {
// 问题出在ps.getParameterMetaData()调用上
sqlTypeToUse = ps.getParameterMetaData().getParameterType(paramIndex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("JDBC 3.0 getParameterType call not supported - using fallback method instead: " + ex);
}
}
}
if (sqlTypeToUse == null) {
// JDBC driver not compliant with JDBC 3.0 -> proceed with database-specific checks
sqlTypeToUse = Types.NULL;
try {
if (dbmd == null) {
dbmd = ps.getConnection().getMetaData();
}
if (jdbcDriverName == null) {
jdbcDriverName = dbmd.getDriverName();
}
if (shouldIgnoreGetParameterType == null) {
// Register JDBC driver with no support for getParameterType, except for the
// Oracle 12c driver where getParameterType fails for specific statements only
// (so an exception thrown above does not indicate general lack of support).
driversWithNoSupportForGetParameterType.add(jdbcDriverName);
}
String databaseProductName = dbmd.getDatabaseProductName();
if (databaseProductName.startsWith("Informix") ||
(jdbcDriverName.startsWith("Microsoft") && jdbcDriverName.contains("SQL Server"))) {
// "Microsoft SQL Server JDBC Driver 3.0" versus "Microsoft JDBC Driver 4.0 for SQL Server"
useSetObject = true;
}
else if (databaseProductName.startsWith("DB2") ||
jdbcDriverName.startsWith("jConnect") ||
jdbcDriverName.startsWith("SQLServer")||
jdbcDriverName.startsWith("Apache Derby")) {
sqlTypeToUse = Types.VARCHAR;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.debug("Could not check connection metadata", ex);
}
}
if (useSetObject) {
ps.setObject(paramIndex, null);
}
else {
ps.setNull(paramIndex, sqlTypeToUse);
}
}
else if (typeName != null) {
ps.setNull(paramIndex, sqlType, typeName);
}
else {
ps.setNull(paramIndex, sqlType);
}
}
PgPreparedStatement
public ParameterMetaData getParameterMetaData() throws SQLException {
int flags = QueryExecutor.QUERY_ONESHOT | QueryExecutor.QUERY_DESCRIBE_ONLY
| QueryExecutor.QUERY_SUPPRESS_BEGIN;
StatementResultHandler handler = new StatementResultHandler();
connection.getQueryExecutor().execute(preparedQuery.query, preparedParameters, handler, 0, 0,
flags);
int[] oids = preparedParameters.getTypeOIDs();
return createParameterMetaData(connection, oids);
}
QueryExecutorImpl
private void sendOneQuery(SimpleQuery query, SimpleParameterList params, int maxRows,
int fetchSize, int flags) throws IOException {
boolean asSimple = (flags & QueryExecutor.QUERY_EXECUTE_AS_SIMPLE) != 0;
if (asSimple) {
assert (flags & QueryExecutor.QUERY_DESCRIBE_ONLY) == 0
: "Simple mode does not support describe requests. sql = " + query.getNativeSql()
+ ", flags = " + flags;
sendSimpleQuery(query, params);
return;
}
assert !query.getNativeQuery().multiStatement
: "Queries that might contain ; must be executed with QueryExecutor.QUERY_EXECUTE_AS_SIMPLE mode. "
+ "Given query is " + query.getNativeSql();
// Per https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/protocol-flow.html#PROTOCOL-FLOW-EXT-QUERY
// A Bind message can use the unnamed prepared statement to create a named portal.
// If the Bind is successful, an Execute message can reference that named portal until either
// the end of the current transaction
// or the named portal is explicitly destroyed
boolean noResults = (flags & QueryExecutor.QUERY_NO_RESULTS) != 0;
boolean noMeta = (flags & QueryExecutor.QUERY_NO_METADATA) != 0;
boolean describeOnly = (flags & QueryExecutor.QUERY_DESCRIBE_ONLY) != 0;
// extended queries always use a portal
// the usePortal flag controls whether or not we use a *named* portal
boolean usePortal = (flags & QueryExecutor.QUERY_FORWARD_CURSOR) != 0 && !noResults && !noMeta
&& fetchSize > 0 && !describeOnly;
boolean oneShot = (flags & QueryExecutor.QUERY_ONESHOT) != 0;
boolean noBinaryTransfer = (flags & QUERY_NO_BINARY_TRANSFER) != 0;
boolean forceDescribePortal = (flags & QUERY_FORCE_DESCRIBE_PORTAL) != 0;
// Work out how many rows to fetch in this pass.
int rows;
if (noResults) {
rows = 1; // We're discarding any results anyway, so limit data transfer to a minimum
} else if (!usePortal) {
rows = maxRows; // Not using a portal -- fetchSize is irrelevant
} else if (maxRows != 0 && fetchSize > maxRows) {
// fetchSize > maxRows, use maxRows (nb: fetchSize cannot be 0 if usePortal == true)
rows = maxRows;
} else {
rows = fetchSize; // maxRows > fetchSize
}
sendParse(query, params, oneShot);
// Must do this after sendParse to pick up any changes to the
// query's state.
//
boolean queryHasUnknown = query.hasUnresolvedTypes();
boolean paramsHasUnknown = params.hasUnresolvedTypes();
boolean describeStatement = describeOnly
|| (!oneShot && paramsHasUnknown && queryHasUnknown && !query.isStatementDescribed());
if (!describeStatement && paramsHasUnknown && !queryHasUnknown) {
int[] queryOIDs = castNonNull(query.getPrepareTypes());
int[] paramOIDs = params.getTypeOIDs();
for (int i = 0; i < paramOIDs.length; i++) {
// Only supply type information when there isn't any
// already, don't arbitrarily overwrite user supplied
// type information.
if (paramOIDs[i] == Oid.UNSPECIFIED) {
params.setResolvedType(i + 1, queryOIDs[i]);
}
}
}
if (describeStatement) {
sendDescribeStatement(query, params, describeOnly);
if (describeOnly) {
return;
}
}
// Construct a new portal if needed.
Portal portal = null;
if (usePortal) {
String portalName = "C_" + (nextUniqueID++);
portal = new Portal(query, portalName);
}
sendBind(query, params, portal, noBinaryTransfer);
// A statement describe will also output a RowDescription,
// so don't reissue it here if we've already done so.
//
if (!noMeta && !describeStatement) {
/*
* don't send describe if we already have cached the row description from previous executions
*
* XXX Clearing the fields / unpreparing the query (in sendParse) is incorrect, see bug #267.
* We might clear the cached fields in a later execution of this query if the bind parameter
* types change, but we're assuming here that they'll still be valid when we come to process
* the results of this query, so we don't send a new describe here. We re-describe after the
* fields are cleared, but the result of that gets processed after processing the results from
* earlier executions that we didn't describe because we didn't think we had to.
*
* To work around this, force a Describe at each execution in batches where this can be a
* problem. It won't cause more round trips so the performance impact is low, and it'll ensure
* that the field information available when we decoded the results. This is undeniably a
* hack, but there aren't many good alternatives.
*/
if (!query.isPortalDescribed() || forceDescribePortal) {
sendDescribePortal(query, portal);
}
}
sendExecute(query, portal, rows);
}
通过以上分析,可以确认针对每个值为null的字段,多发送了Parse、Describe、Execute、Sync报文。
Parse
Describe
解决方法
通过以上分析可知,造成流量增大的原因是Spring JdbcTemplate中针对值为null的字段,调用了PgPreparedStatement.getParameterMetaData导致的。
所以规避方式是不触发这个调用。
方法一
自定义字段的设置方式的实现类。
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, new PreparedStatementSetter() {
@Override
public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
ps.setString(1,null);
ps.setString(2,null);
ps.setInt(3,1);
}
});
方法二
依然调用原有JdbcTemplate方法,需要保证字段值不为null;
方法三
依然调用原有JdbcTemplate方法,JVM启动参数配置(需测试):
-Dspring.jdbc.getParameterType.ignore=true
MySQL JDBC Driver
MySQL JDBC Driver是否存在这个问题?经过分析相关代码,及ECS带宽流量,可以确定不存在这个问题。
public ParameterMetaData getParameterMetaData() throws SQLException {
synchronized (checkClosed().getConnectionMutex()) {
if (this.parameterMetaData == null) {
if (this.connection.getGenerateSimpleParameterMetadata()) {
this.parameterMetaData = new MysqlParameterMetadata(this.parameterCount);
} else {
this.parameterMetaData = new MysqlParameterMetadata(null, this.parameterCount, getExceptionInterceptor());
}
}
return this.parameterMetaData;
}
}