源码分析Dubbo集群策略原创
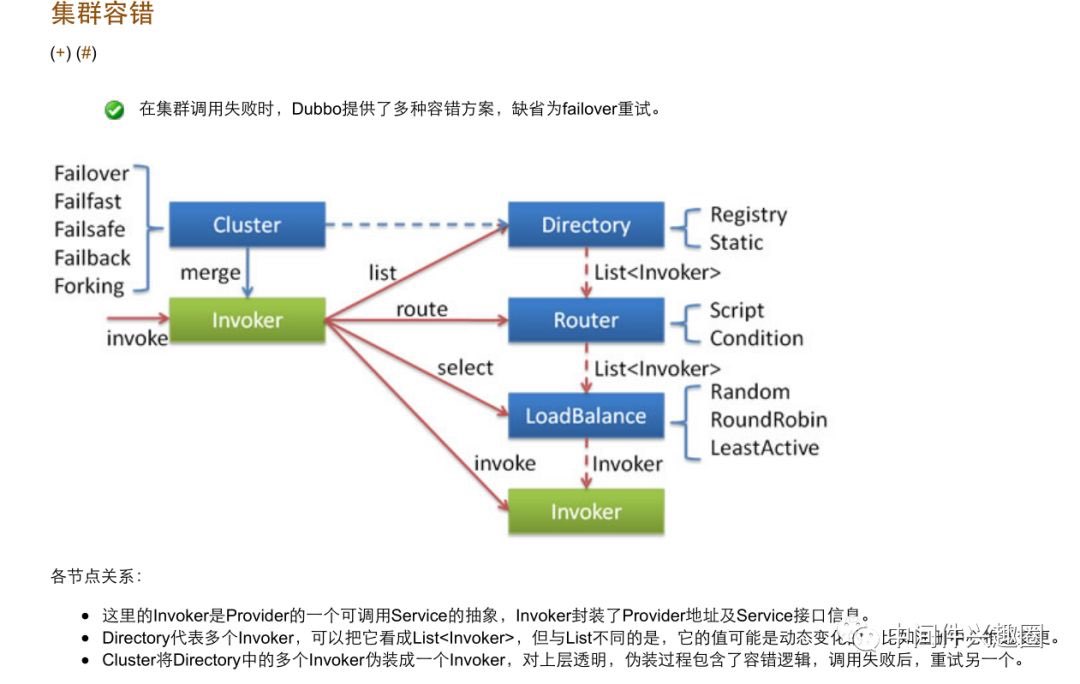
前面的文章,已经单独对服务发现(Directory、RegistryDirectory)、路由机制(Router)、负载均衡机制(LoadBalance),本节将重点分析集群容错机制(AbstractClusterInvoker)。整个集群容错中,上述组件扮演的角色见下图所示,本文将重点分析AbstractClusterInvoker是如何融合这些组件的。
AbstractClusterInvoker#invoke
1@Override
2 public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
3 checkWhetherDestroyed();
4 LoadBalance loadbalance = null;
5 List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation); // @1
6 if (invokers != null && !invokers.isEmpty()) {
7 loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(invokers.get(0).getUrl()
8 .getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.LOADBALANCE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE)); // @2
9 }
10 RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
11 return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance); // @3
12 }
- 代码@1:根据调用上下文,获取服务提供者列表,服务提供者从Directory中获取。
1protected List<Invoker<T>> list(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
2 List<Invoker<T>> invokers = directory.list(invocation);
3 return invokers;
4 }
最终会调用RegistryDirecotry的list方法,该方法的服务提供者是当该消费者订阅的服务的服务提供者列表发送变化后,会在注册中心产生事件,然后通知消费者更新服务提供者列表(本地缓存)。需要注意的是RegistryDirecotry在返回Invoker之前,已经使用Router进行了一次筛选,具体实现在RegistryDirectory#notify方法时。
-
代码@2:根据SPI机制,获取负载均衡算法的实现类,根据< dubbo:consumer loadbalance=""/>、< dubbo:reference loadbalance=""/>等标签的配置值,默认为random,加权随机算法。
-
代码@3:根据调用上下文,服务提供者列表,负载均衡算法选择一服务提供者,具体代码由AbstractClusterInvoker的各个子类实现。
Dubbo目前支持的集群容错策略在中/dubbo-cluster/src/main/resources/META-INF/dubbo/internal/com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster定义,具体内容如下:
1mock=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.wrapper.MockClusterWrapper
2failover=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.FailoverCluster
3failfast=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.FailfastCluster
4failsafe=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.FailsafeCluster
5failback=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.FailbackCluster
6forking=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.ForkingCluster
7available=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.AvailableCluster
8mergeable=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.MergeableCluster
9broadcast=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.BroadcastCluster
上述各种集群策略,对应的执行器为Cluser+Invoker,例如FailoverCluster对应的Invoker为:FailoverClusterInvoker。
在讲解各种集群容错策略之前,我们首先关注一下AbstractClusterInvoker具体从服务提供者中按照不同的负载均衡算法选取服务提供者的算法。
AbstractClusterInvoker#select
1protected Invoker<T> select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws
2 RpcException { // @1
3 if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty())
4 return null;
5 String methodName = invocation == null ? "" : invocation.getMethodName();
6 boolean sticky = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.CLUSTER_STICKY_KEY,
7 Constants.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_STICKY); // @2
8 {
9 //ignore overloaded method
10 if (stickyInvoker != null && !invokers.contains(stickyInvoker)) {
11 stickyInvoker = null;
12 }
13 //ignore concurrency problem
14 if (sticky && stickyInvoker != null && (selected == null || !selected.contains(stickyInvoker))) {
15 if (availablecheck && stickyInvoker.isAvailable()) {
16 return stickyInvoker;
17 }
18 }
19 }
20 Invoker<T> invoker = doSelect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected); // @3
21
22 if (sticky) {
23 stickyInvoker = invoker;
24 }
25 return invoker;
26 }
-
代码@1:参数说明
- LoadBalance loadbalance:负载均衡算法。
- Invocation invocation:服务调用上下文环境。
- List< Invoker< T>> invokers:待选的服务提供者列表。
-
List< Invoker< T>> selected:本次集群测试,已选择的服务提供者。
-
代码@2:sticky机制(粘性),如果开启了粘性机制的话。通过< dubbo:method sticky=“true”/>,默认不开启。如果开启,上一次该服务调用的是哪个服务提供者,只要调用过程中不发生错误,后续都会选择该服务提供者进行调用。
-
代码@3:执行doSelect选择。
AbstractClusterInvoker#doSelect
1private Invoker<T> doSelect(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
2 if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty())
3 return null;
4 if (invokers.size() == 1) // @1
5 return invokers.get(0);
6 // If we only have two invokers, use round-robin instead.
7 if (invokers.size() == 2 && selected != null && !selected.isEmpty()) { // @2
8 return selected.get(0) == invokers.get(0) ? invokers.get(1) : invokers.get(0);
9 }
10 if (loadbalance == null) {
11 loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE);
12 }
13 Invoker<T> invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, getUrl(), invocation); // @3
14
15 //If the `invoker` is in the `selected` or invoker is unavailable && availablecheck is true, reselect.
16 if ((selected != null && selected.contains(invoker))
17 || (!invoker.isAvailable() && getUrl() != null && availablecheck)) {
18 try {
19 Invoker<T> rinvoker = reselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected, availablecheck); // @4
20 if (rinvoker != null) {
21 invoker = rinvoker;
22 } else {
23 //Check the index of current selected invoker, if it's not the last one, choose the one at index+1.
24 int index = invokers.indexOf(invoker);
25 try {
26 //Avoid collision
27 invoker = index < invokers.size() - 1 ? invokers.get(index + 1) : invoker;
28 } catch (Exception e) {
29 logger.warn(e.getMessage() + " may because invokers list dynamic change, ignore.", e);
30 }
31 }
32 } catch (Throwable t) {
33 logger.error("cluster reselect fail reason is :" + t.getMessage() + " if can not solve, you can set cluster.availablecheck=false in url", t);
34 }
35 }
36 return invoker;
37 }
- 代码@1:如果可选Invoker只有一个的话,直接返回该Invoker。
- 代码@2:如果只有两个Invoker,并且其中一个已被选择,返回另外一个未选择的Invoker。
- 代码@3:调用loadBalance负载均衡算法,选择一个服务提供者。
- 代码@4:如果选择的Invoker已被选择,则重新选择,这里有一个疑问,为什么不在选之前,先过滤掉已被选的Invoker。
从服务提供者列表中选择一个服务提供者算法就介绍到这里,接下来将一一分析Dubbo提供的集群容错方式。
接下来从源码角度详细分析Dubbo集群策略的实现原理。
FailoverCluster
策略:失败后自动选择其他服务提供者进行重试,重试次数由retries属性设置,< dubbo:reference retries = “2”/>设置,默认为2,代表重试2次,最多执行3次。是Dubbo集群容错的默认模式,其具体实现为FailoverClusterInvoker。
FailoverClusterInvoker#doInvoke
1 public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
2 List<Invoker<T>> copyinvokers = invokers;
3 checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
4 int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.RETRIES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1; // @1
5 if (len <= 0) {
6 len = 1;
7 }
8 // retry loop.
9 RpcException le = null; // last exception.
10 List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyinvokers.size()); // invoked invokers.
11 Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len); // @2
12 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { // @3
13 //Reselect before retry to avoid a change of candidate `invokers`.
14 //NOTE: if `invokers` changed, then `invoked` also lose accuracy.
15 if (i > 0) { // @4
16 checkWhetherDestroyed();
17 copyinvokers = list(invocation);
18 // check again
19 checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
20 }
21 Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyinvokers, invoked); // @5
22 invoked.add(invoker);
23 RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked);
24 try {
25 Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation); // @6
26 if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
27 logger.warn("Although retry the method " + invocation.getMethodName()
28 + " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
29 + " was successful by the provider " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress()
30 + ", but there have been failed providers " + providers
31 + " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
32 + ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
33 + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
34 + " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
35 + le.getMessage(), le);
36 }
37 return result;
38 } catch (RpcException e) {
39 if (e.isBiz()) { // biz exception.
40 throw e;
41 }
42 le = e;
43 } catch (Throwable e) {
44 le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
45 } finally {
46 providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress()); // @7
47 }
48 }
49 throw new RpcException(le != null ? le.getCode() : 0, "Failed to invoke the method "
50 + invocation.getMethodName() + " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
51 + ". Tried " + len + " times of the providers " + providers
52 + " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
53 + ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
54 + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version "
55 + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
56 + (le != null ? le.getMessage() : ""), le != null && le.getCause() != null ? le.getCause() : le);
57 }
- 代码@1:首先校验服务提供者列表,如果为空,则抛出RpcException,提示没有可用的服务提供者。
- 代码@2:构建Set< Stirng> providers,主要用来已调用服务提供者的地址,如果本次调用失败,将在日志信息中打印已调用的服务提供者信息。
- 代码@3,循环执行次数,等于retries + 1 次。
- 代码@4:如果i>0,表示服务调用,在重试,此时需要重新调用Directory#list方法,获取最小的服务提供者列表。
- 代码@5:根据负载均衡算法,选择Invoker,后续详细分析。
- 代码@6:根据负载算法,路由算法从服务提供者列表选一个服务提供者,发起RPC调用。
- 代码@7:将本次服务提供者的地址添加到providers集合中,如果多次重试后,无法完成正常的调用,将在错误日志中包含这些信息。
AvailableClusterInvoker
- 策略:选择集群第一个可用的服务提供者。
- 缺点:相当于服务的主备,但同时只有一个服务提供者承载流量,并没有使用集群的负载均衡机制。
AvailableClusterInvoker#doInvoke
1public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
2 for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
3 if (invoker.isAvailable()) {
4 return invoker.invoke(invocation);
5 }
6 }
7 throw new RpcException("No provider available in " + invokers);
8}
遍历服务提供者列表,选择第一个可用服务提供者,然后执行RPC服务调用,如果调用失败,则失败。
BroadcastClusterInvoker
策略:广播调用,将调用所有服务提供者,一个服务调用者失败,并不会熔断,并且一个服务提供者调用失败,整个调用认为失败。
场景:刷新缓存。
1public Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
2 checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); // @1
3 RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invokers);
4 RpcException exception = null;
5 Result result = null;
6 for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) { // @2
7 try {
8 result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
9 } catch (RpcException e) {
10 exception = e;
11 logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
12 } catch (Throwable e) {
13 exception = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
14 logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
15 }
16 }
17 if (exception != null) { // @3
18 throw exception;
19 }
20 return result;
21 }
- 代码@1:检测服务提供者列表,如果为空,则抛出没有服务提供的异常。
- 代码@2:遍历服务提供者列表,依次调用服务提供者的invoker,每个服务调用用try catch语句包裹,当服务调用发生异常时,记录异常信息,但并不立即返回,广播模式,每个服务提供者调用是异步还是同步,取决服务调用的配置,默认是同步调用。
- 代码@3:只要其中一个服务调用发送一次,将抛出异常 信息,异常信息被封装为RpcException。
FailbackClusterInvoker
策略:调用失败后,返回成功,但会在后台定时重试,重试次数(反复)
场景:通常用于消息通知,但消费者重启后,重试任务丢失。
FailbackClusterInvoker#doInvoke
1protected Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
2 try {
3 checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); // @1
4 Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null); // @2
5 return invoker.invoke(invocation); // @3
6 } catch (Throwable e) {
7 logger.error("Failback to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", wait for retry in background. Ignored exception: "
8 + e.getMessage() + ", ", e);
9 addFailed(invocation, this); // @4
10 return new RpcResult(); // ignore
11 }
12 }
- 代码@1:校验服务提供者列表,如果为空,则抛出没有服务提供者错误。
- 代码@2:根据负载均衡机制,选择一个服务提供者。
- 代码@3:发起远程服务调用,如果出现异常,调用addFailed方法,添加重试任务,然后返回给调用方成功。
接下来看一下addFailed方法。
FailbackClusterInvoker#addFailed
1private void addFailed(Invocation invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?> router) { // @1
2 if (retryFuture == null) { // @2
3 synchronized (this) {
4 if (retryFuture == null) {
5 retryFuture = scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() { // @3
6
7 @Override
8 public void run() {
9 // collect retry statistics
10 try {
11 retryFailed();
12 } catch (Throwable t) { // Defensive fault tolerance
13 logger.error("Unexpected error occur at collect statistic", t);
14 }
15 }
16 }, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
17 }
18 }
19 }
20 failed.put(invocation, router); // @4
21 }
- 代码@1:Invocation invocation:调用上下文;AbstractClusterInvoker< ?> router:调用集群策略。
- 代码@2:如果retryFuture(ScheduledFuture< ?> retryFuture)为空,则加锁创建一个定时调度任务,任务以每隔5s的频率调用retryFailed方法。
- 代码@3:添加重试任务(ConcurrentMap< Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker< ?>> failed)。想必retryFailed方法就是遍历failed,一个一个重复调用,如果调用成功则移除,调用不成功,继续放入。
FailbackClusterInvoker#retryFailed
1void retryFailed() {
2 if (failed.size() == 0) {
3 return;
4 }
5 for (Map.Entry<Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?>> entry : new HashMap<Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?>>( // @1
6 failed).entrySet()) {
7 Invocation invocation = entry.getKey();
8 Invoker<?> invoker = entry.getValue();
9 try {
10 invoker.invoke(invocation); // @2
11 failed.remove(invocation); // @3
12 } catch (Throwable e) {
13 logger.error("Failed retry to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", waiting again.", e);
14 }
15 }
16 }
- 代码@1:遍历待重试列表,然后发起远程调用,如果调用成功,则从集合中移除,如果只选失败,并不会从待重试列表中移除,也就是在消费端不重启的情况下,会一直重复调用,直到成功。
FailfastClusterInvoker
策略:快速失败,服务调用失败后立马抛出异常,不进行重试。
场景:是否修改类服务(未实行幂等的服务调用)
1public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
2 checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); // @1
3 Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null); // @2
4 try {
5 return invoker.invoke(invocation); // @3
6 } catch (Throwable e) {
7 if (e instanceof RpcException && ((RpcException) e).isBiz()) { // biz exception.
8 throw (RpcException) e;
9 }
10 throw new RpcException(e instanceof RpcException ? ((RpcException) e).getCode() : 0, "Failfast invoke providers " + invoker.getUrl() + " " +
11 loadbalance.getClass().getSimpleName() + " select from all providers " + invokers + " for service " + getInterface().getName() + " method " +
12 invocation.getMethodName() + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", but no luck to
13 perform the invocation. Last error is: " + e.getMessage(), e.getCause() != null ? e.getCause() : e); // @4
14 }
15 }
- 代码@1:检查服务提供者,如果服务提供者列表为空,抛出没有服务提供者错误。
- 代码@2:根据负载算法选择一个服务提供者。
- 代码@3:发起RPC服务调用。
- 代码@4:如果服务调用异常,抛出异常,打印服务消费者,服务提供者信息。
FailsafeClusterInvoker
策略:服务调用失败后,只打印错误日志,然后返回服务调用成功。
场景:调用审计,日志类服务接口。
FailsafeClusterInvoker#doInvoke
1public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
2 try {
3 checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); // @1
4 Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null); // @2
5 return invoker.invoke(invocation); // @3
6 } catch (Throwable e) {
7 logger.error("Failsafe ignore exception: " + e.getMessage(), e);
8 return new RpcResult(); // ignore
9 }
10}
- 代码@1:检查服务提供者,如果服务提供者列表为空,抛出没有服务提供者错误。
- 代码@2:根据负载算法选择一个服务提供者。
- 代码@3:发起RPC服务调用,如果出现异常,记录错误堆栈信息,并返回成功。
ForkingClusterInvoker
策略:并行调用多个服务提供者,当一个服务提供者返回成功,则返回成功。
场景:实时性要求比较高的场景,但浪费服务器资源,通常可以通过forks参数设置并发调用度。
ForkingClusterInvoker#doInvoke
1public Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
2 checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); // @1
3 final List<Invoker<T>> selected;
4 final int forks = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.FORKS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_FORKS); // @2
5 final int timeout = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
6 if (forks <= 0 || forks >= invokers.size()) {
7 selected = invokers;
8 } else {
9 selected = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>();
10 for (int i = 0; i < forks; i++) {
11 // TODO. Add some comment here, refer chinese version for more details.
12 Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
13 if (!selected.contains(invoker)) {//Avoid add the same invoker several times.
14 selected.add(invoker);
15 }
16 }
17 }
18 RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) selected);
19 final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
20 final BlockingQueue<Object> ref = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Object>();
21 for (final Invoker<T> invoker : selected) { // @3
22 executor.execute(new Runnable() {
23 @Override
24 public void run() {
25 try {
26 Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
27 ref.offer(result);
28 } catch (Throwable e) {
29 int value = count.incrementAndGet();
30 if (value >= selected.size()) {
31 ref.offer(e);
32 }
33 }
34 }
35 });
36 }
37 try {
38 Object ret = ref.poll(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // @4
39 if (ret instanceof Throwable) {
40 Throwable e = (Throwable) ret;
41 throw new RpcException(e instanceof RpcException ? ((RpcException) e).getCode() : 0, "Failed to forking invoke provider " + selected + ", but no luck to perform the invocation. Last error is: " + e.getMessage(), e.getCause() != null ? e.getCause() : e);
42 }
43 return (Result) ret;
44 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
45 throw new RpcException("Failed to forking invoke provider " + selected + ", but no luck to perform the invocation. Last error is: " + e.getMessage(), e);
46 }
47 }
- 代码@1:检查服务提供者,如果服务提供者列表为空,抛出没有服务提供者错误。
- 代码@2:获取forks属性,貌似只能通过在< dubbo:reference />用< dubbo:parameter key=“forks” value=""/>来设置forks,其默认值为2,如果forks值大于服务提供者的数量,则将调用所有服务提供者,如果forks值小于服务提供者的数量,则使用负载均衡算法,选择forks个服务提供者。
- 代码@3:依次异步向服务提供者发起RPC调用,并将结果添加到BlockingQueue< Object> ref,如果服务调用发送错误,并且发生错误的个数大于等于本次调用的个数,则将错误信息放入BlockingQueue< Object> ref,否则,将错误数增加1。
- 代码@4:Object ret = ref.poll(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS),从该队列中获取结果,如果队列未空,则会阻塞等待,直到超时,当有一个调用成功后,将返回,忽略其他调用结果。
本文重点分析了Dubbo集群容错机制,路由发现、路由算法、负载均衡等是如何共同协作完成Dubbo的服务调用,并详细分析了Dubbo各种集群策略,例如failover、failfast、failsafe、failback、forking、available等实现细节。