如何在SpringBoot中使用异步方法优化Service逻辑提高接口响应速度?转载
3年前
466503
Part1为什么需要异步方法?
先说结论: 合理使用异步方法可以让业务接口快到飞起!
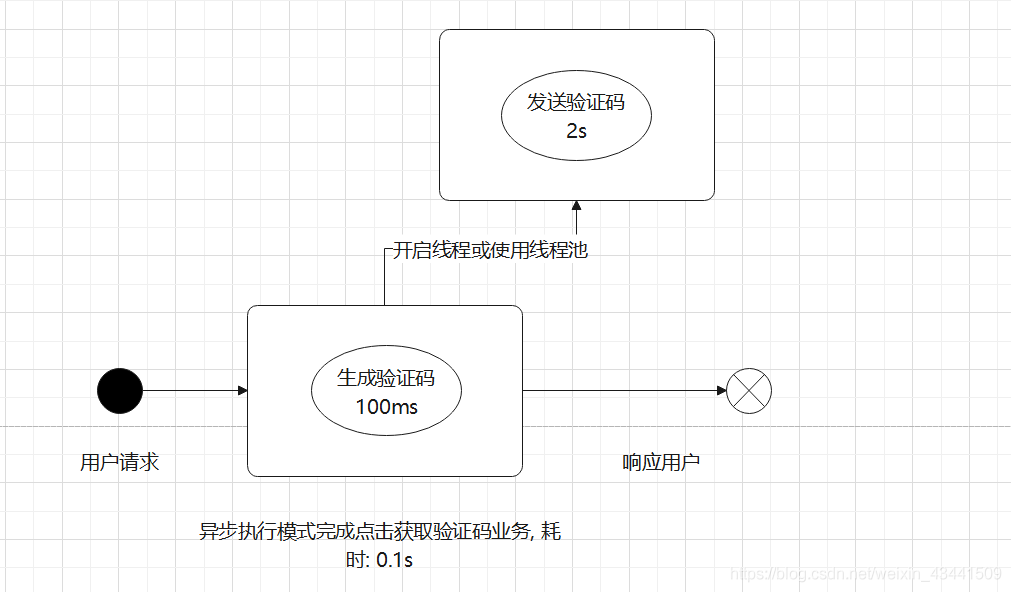
异步方法适用于逻辑与逻辑之间可以相互分割互不影响的业务中, 如生成验证码和发送验证码组成的业务, 其实无需等到真正发送成功验证码才对客户端进行响应, 可以让短信发送这一耗时操作转为异步执行, 解耦耗时操作和核心业务; 同理还有文章阅读的业务逻辑 = 查询文章详情 + 更新文章阅读量后再响应客户端, 其实也无需等到阅读量更新后才响应文章详情给客户端, 用户查看文章是主要逻辑, 而文章阅读量更新是次要逻辑, 况且阅读量就算更新失败一点数据偏差也不会影响用户阅读因此这两个数据库操作之间的一致性是较弱的, 这类都能用异步事件去优化. 所以说: 恰当的在我们的Service中加入异步方法能大大提高接口的响应速度, 提升用户体验!
同步执行(同在一个线程中):
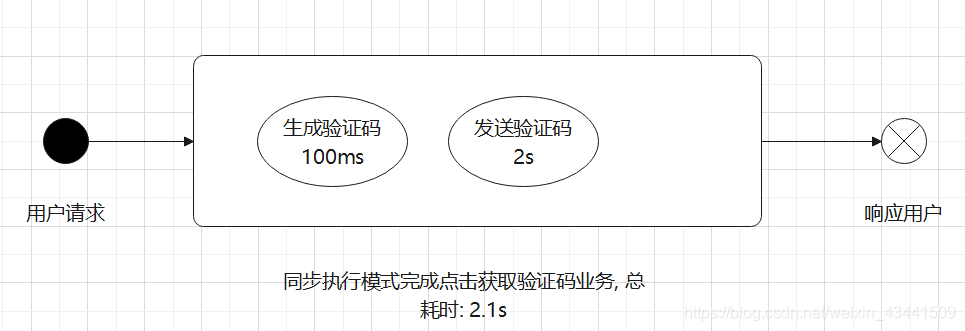
异步执行(开启额外线程来执行):
Part2SpringBoot中的异步方法支持
其实, 在SpringBoot中并不需要我们自己去创建维护线程或者线程池来异步的执行方法, SpringBoot已经提供了异步方法支持注解.
@EnableAsync // 使用异步方法时需要提前开启(在启动类上或配置类上)
@Async // 被async注解修饰的方法由SpringBoot默认线程池(SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor)执行
比如使用Spring的异步支持实现文章查询并增加阅读量
Service层:
@Service
public class ArticleServiceImpl {
// 查询文章
public String selectArticle() {
// TODO 模拟文章查询操作
System.out.println("查询任务线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "文章详情";
}
// 文章阅读量+1
@Async
public void updateReadCount() {
// TODO 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("更新任务线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
Controller层:
@RestController
public class AsyncTestController {
@Autowired
private ArticleServiceImpl articleService;
/**
* 模拟获取文章后阅读量+1
*/
@PostMapping("/article")
public String getArticle() {
// 查询文章
String article = articleService.selectArticle();
// 阅读量+1
articleService.updateReadCount();
System.out.println("文章阅读业务执行完毕");
return article;
}
}
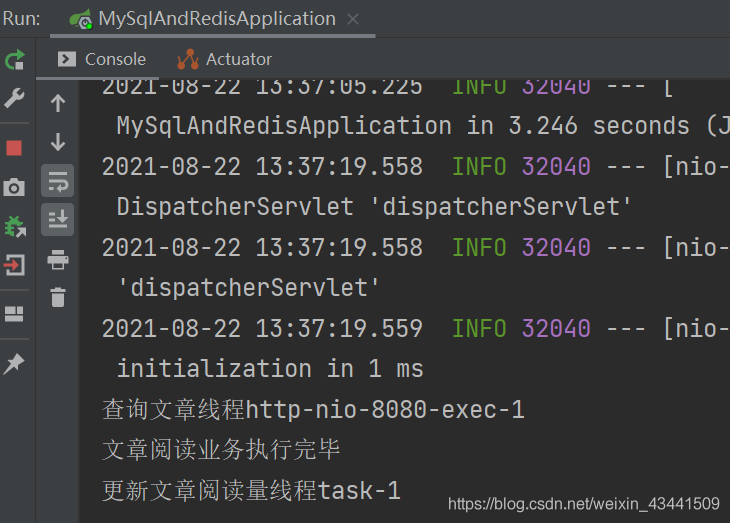
测试结果: 我们可以感受到接口响应速度大大提升, 而且从日志中key看到两个执行任务是在不同的线程中执行的
Part3自定义线程池执行异步方法
SpringBoot为我们默认提供了线程池(SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor)来执行我们的异步方法, 我们也可以自定义自己的线程池.
第一步配置自定义线程池
@EnableAsync // 开启多线程, 项目启动时自动创建
@Configuration
public class AsyncConfig {
@Bean("customExecutor")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncOperationExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 设置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(8);
// 设置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
// 设置队列大小
executor.setQueueCapacity(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 设置线程活跃时间(秒)
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
// 设置线程名前缀+分组名称
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("AsyncOperationThread-");
executor.setThreadGroupName("AsyncOperationGroup");
// 所有任务结束后关闭线程池
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// 初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
第二步, 在@Async注解上指定执行的线程池即可
// 文章阅读量+1
@Async("customExecutor")
public void updateReadCount() {
// TODO 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("更新文章阅读量线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
Part4如何捕获(无返回值的)异步方法中的异常
-
以实现 AsyncConfigurer接口的getAsyncExecutor方法和getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler方法改造配置类 -
自定义异常处理类 CustomAsyncExceptionHandler
@EnableAsync // 开启多线程, 项目启动时自动创建
@Configuration
public class AsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 设置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(8);
// 设置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
// 设置队列大小
executor.setQueueCapacity(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 设置线程活跃时间(秒)
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
// 设置线程名前缀+分组名称
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("AsyncOperationThread-");
executor.setThreadGroupName("AsyncOperationGroup");
// 所有任务结束后关闭线程池
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// 初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return new CustomAsyncExceptionHandler();
}
}
public class CustomAsyncExceptionHandler implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable throwable, Method method, Object... obj) {
System.out.println("异常捕获---------------------------------");
System.out.println("Exception message - " + throwable.getMessage());
System.out.println("Method name - " + method.getName());
for (Object param : obj) {
System.out.println("Parameter value - " + param);
}
System.out.println("异常捕获---------------------------------");
}
}
Part5如何获取(有返回值)异步方法的返回值
使用Future类及其子类来接收异步方法返回值 注意:
-
无返回值的异步方法抛出异常不会影响Controller的主要业务逻辑 -
有返回值的异步方法抛出异常会影响Controller的主要业务逻辑
// 异步方法---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Async
public CompletableFuture<Integer> updateReadCountHasResult() {
// TODO 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("更新文章阅读量线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(100 + 1);
}
// Controller调用---------------------------------------------------------------------
@GetMapping("/article")
public String getArticle() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 查询文章
String article = articleService.selectArticle();
// 阅读量+1
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = articleService.updateReadCountHasResult();
int count = 0;
// 循环等待异步请求结果
while (true) {
if(future.isCancelled()) {
System.out.println("异步任务取消");
break;
}
if (future.isDone()) {
count = future.get();
System.out.println(count);
break;
}
}
System.out.println("文章阅读业务执行完毕");
return article + count;
}
Part6异步方法带来的问题/拓展
-
异步方法只能声明在Service方法中在Controller直接调用才会生效, 异步方法被同级Service方法调用不会生效, 很奇怪? -
异步方法 + 事务能顺利执行吗? 或许事务操作应该和异步操作分离开, 被Controller层调用时事务操作在前, 异步操作在后 -
异步方法执行失败后对Controller前半部分的非异步操作无影响, 因此说异步方法在整个业务逻辑中不是100%可靠的, 对于强一致性的业务来说不适用 -
还是消息中间件更为强大, RabbitMQ, Kafka…
作者:jinchange
点赞收藏
分类:


